- What is faceted search and how it works?
- Filters and facets: two ways to narrow search options
- Filters and facets online
- Why use faceted search on your ecommerce site?
- How to index when using faceted filters?
- How to avoid indexing
- Title, H1, and description for faceted search
- Faceted search filter mistakes
- Faceted navigation best practices
- Conclusion
What is faceted search and how it works?
Faceted search, also known as faceted navigation or guided search, is searching and drilling into large datasets (products on an e-commerce site or articles on a news site) by selecting one or more attributes or facets.
Faceted search shows filters or facets for each data attribute (category, price range, size, color, brand, etc.) and users select one or more to narrow down the results to that specific data.
For example, on an e-commerce site, a user is looking for a shirt and starts with a broad search query like “men’s shirt.” The results return thousands of products, but with faceted search, they can narrow down by selecting filters like “long sleeve,” “red,” and “XL” and get a more focused set of results.
Faceted search is searching and discovering and is used everywhere from e-commerce to news sites to applications where large datasets need to be made user-friendly.
Filters and facets: two ways to narrow search options
Filters and facets are both used in e-commerce and other applications to narrow and speed up search results. But they’re different.
Filters remove items from a list based on a condition. For example, on an e-commerce site, a user might want to filter out products that are out of stock or over a certain price. Filters are checkboxes or dropdowns and users select one or more to remove from the results.
Facets group and categorize items based on shared properties or attributes. Users explore search results by narrowing down options by different categories or properties. For example, on an e-commerce site, a user searches for shoes and then uses facets to narrow by brand, size, color, etc.
Filters remove items from a list based on conditions, facets group items based on properties. Both filters and facets.
Here are some examples when filters and facets are used together:
- Category facets: If you have products across multiple categories on your e-commerce site, you can have category facets and filters (e.g., filter by category, price, brand, size).
- Color and size filters with color and size facets: Filter by color and size, and show color and size facets.
- Brand filters with brand facets: Filter by brand and show brand facets.
- Price range filters with price range facets: Filter by price range and show price range facets.
See some examples below.
Filters and facets online
Filters
- Price: Under $50, over $100
- Availability: In stock, out of stock
- Brand: Nike, Adidas, Puma
- Rating: 4+
- Shipping: Free, Expedited
Facets
- Category: Men’s, Women’s, Accessories
- Size: Small, Medium, Large
- Color: Red, Blue, Green
- Material: Cotton, Leather, Polyester
- Style: Casual, Formal, Athletic
Let’s see the best examples of faceted search on ecommerce sites and get inspired to do filters and facets on your site!
Finishline
The online store shows icons for brands in the category:
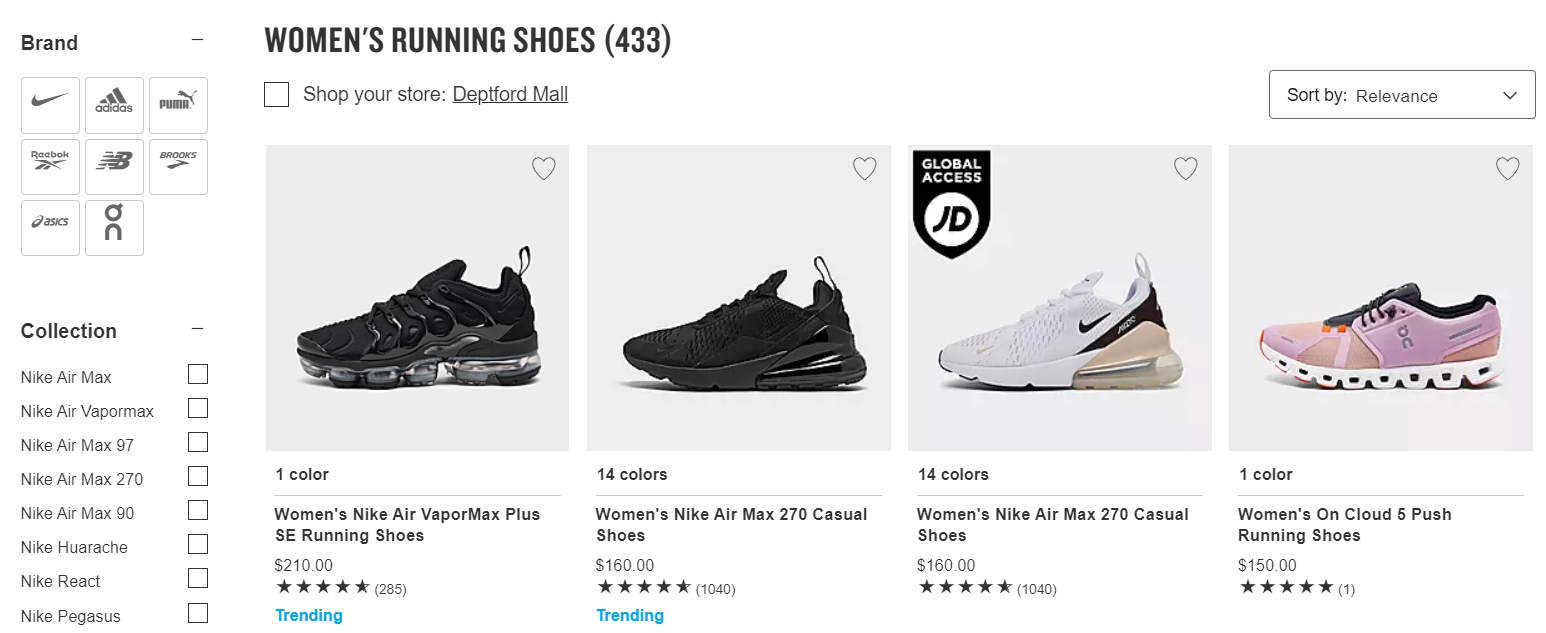
Finishline facets and filters
You can have multiple choices for several facets like size, color, collection, brand, etc. When you select some options, only the matching options remain active in the other facets.

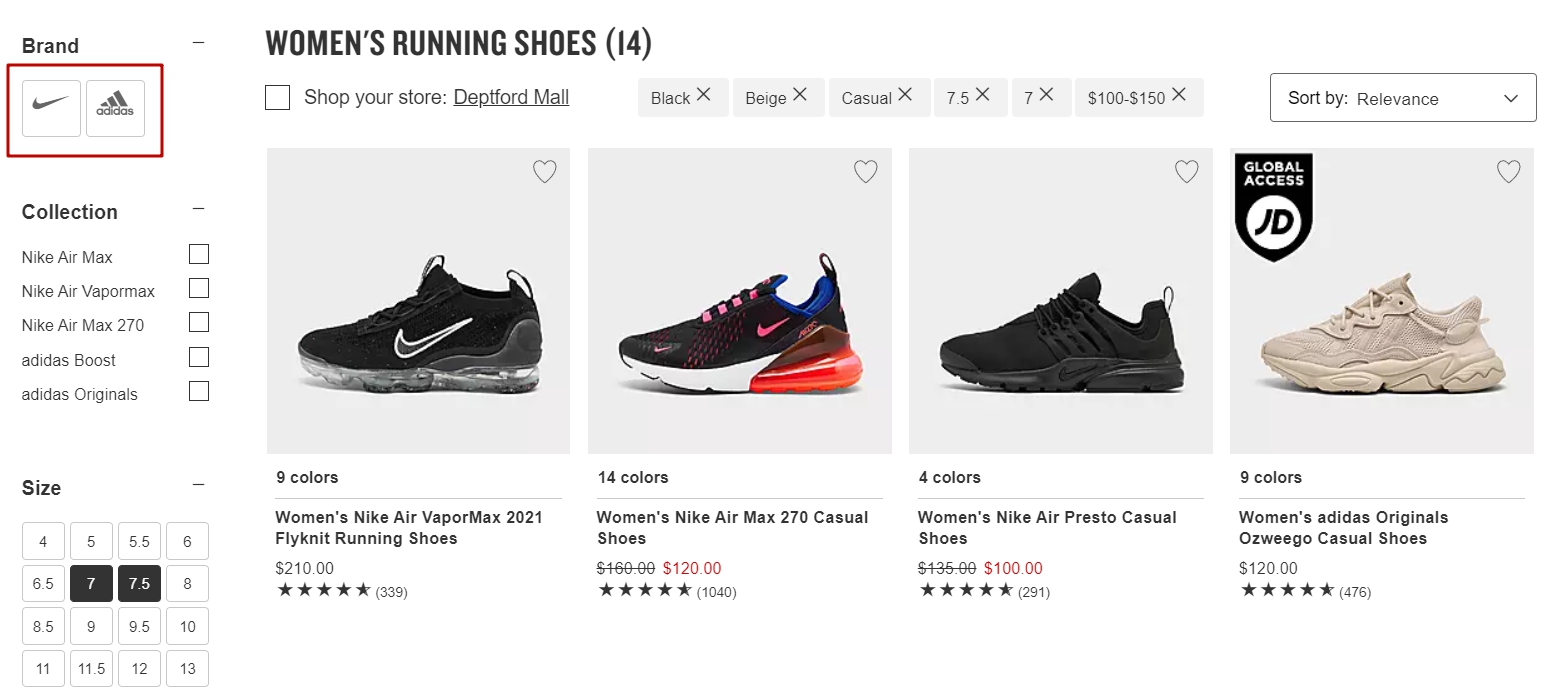
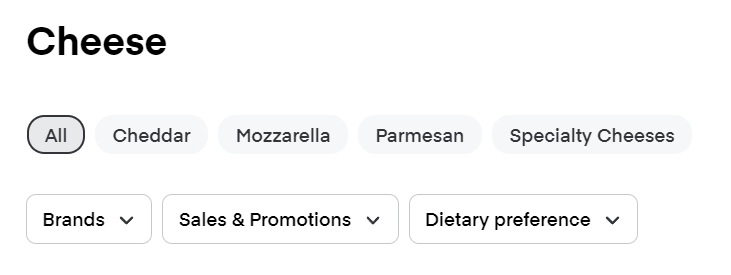
Instacart
A good example of both filters and facets is on instacart.com: go to https://www.instacart.com/store/costco/collections/snack-bars
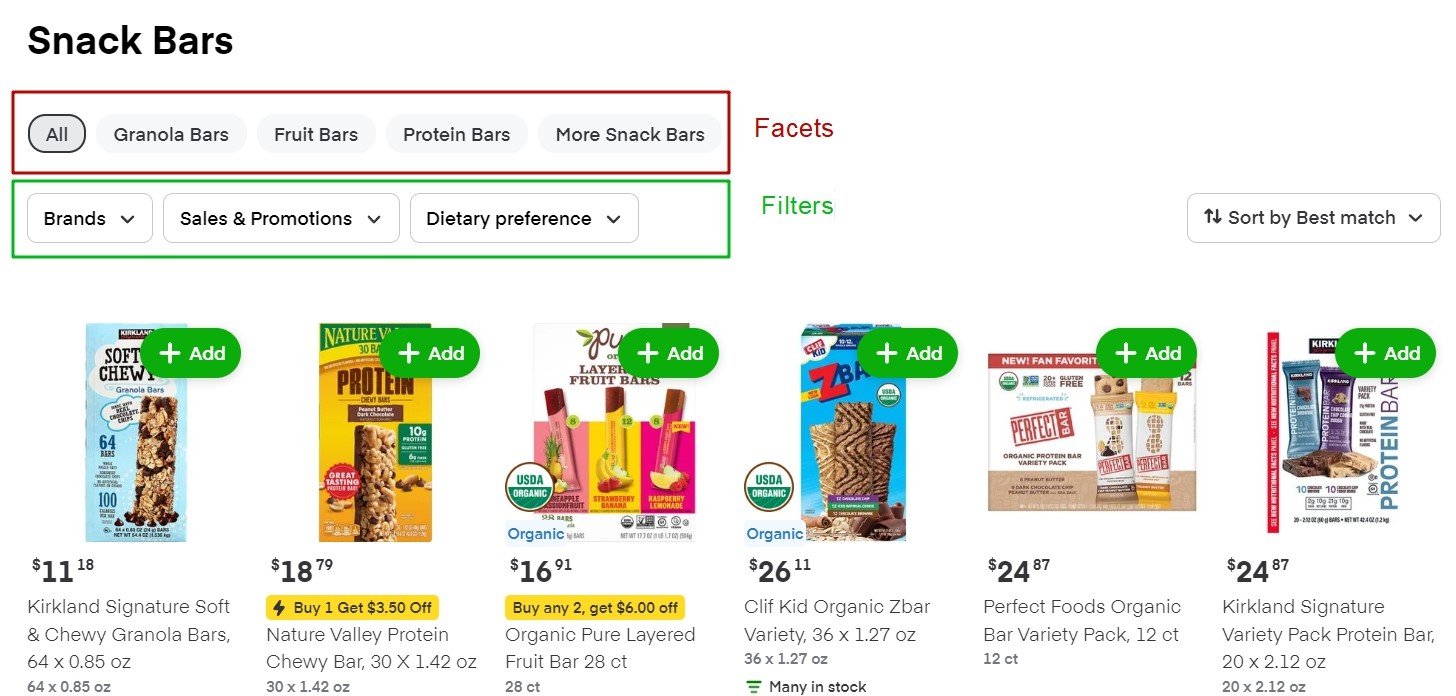
Here are the filters:
- Brands
- Sales & Promotions
- Dietary Preference
They are the same for all the categories.
There are also facets that are unique to this product category:
- Granola Bars
- Fruit Bars
- Protein Bars
- More Snack Bars
Notice that the facets and filters look different visually.
Why use faceted search on your ecommerce site?
- Better user experience: Customers can quickly and easily narrow results by applying filters based on their needs and preferences. Happy customer = more satisfied.
- More engagement and conversions: More relevant results = more engagement and sales.
- Product discovery: Customers discover new products they wouldn’t have found through keyword search alone.
- Competitive advantage: Ecommerce sites with faceted search have an edge over those without. It’s a more user-friendly search.
- Customer loyalty: Easier to find what they’re looking for and discover new = more customer loyalty and repeat business.
How to index when using faceted filters?
You have faceted search on your site, but how do you manage indexing when using faceted filters? If you try to make a search engine index all possible combinations, the number of pages will not be in the thousands, but in the hundreds of thousands. The number of combinations grows exponentially. Too many facets can prevent the faceted pages you really want to index from being indexed.
Here are some SEO best practices for filters and facets:
1. Limitations on properties in parameters
The first restriction is not to index pages if two properties are selected in the same parameter (e.g., size – S and L, color – red and white). Such pages are useless for online store ranking – no one is searching for two parameters at once.
2. Limitations on the number of parameters
Not all parameters that are important for visitors have search volume. Indexing on such parameters can be limited without removing them from faceted filtering.
3. Search parameters, indexing parameters
Not all parameters that are important for visitors have search volume. Indexing on such parameters can be limited without removing them from faceted filtering.
4. Limitations on properties
This rule is similar to the previous one about parameters – not all properties of each parameter should be indexed. This is fine-tuning that’s time-consuming to implement, but will greatly improve the site’s index.
5. Limit of products
Of course, you don’t need to index pages with no products. But do you really need pages with only 1 product found? As a rule, the user experience on such pages is very bad and improves the index. I think you should rank directories with 3 or more products.
How to avoid indexing
1. Rel canonical or noindex
We prefer to specify the main directory page as canonical. But noindex works too.
2. X-Robots-Tag
With this server response, you can avoid indexing of search filters you don’t want to be indexed. It seems to preserve the crawling budget.
3. Rel=”nofollow” for links
Links to filters and facets that shouldn’t be indexed should be prevented from indexing with the nofollow tag.
Title, H1, and description for faceted search
- Title tags are an on-page SEO element and should describe the content of the page. For faceted filter pages, include the main keyword(s) for the page (category or product type being filtered) and the filter being applied. For example, “Men’s Shoes | Athletic Shoes | Nike” would be a good title tag for a page that filters men’s shoes by athletic shoes from the Nike brand.
- For faceted filter pages, the H1 heading should be similar to the title tag and include the main keyword(s) for the page and the filter being applied. For example, “Men’s Athletic Shoes | Nike” would be a good H1 heading for the same page.
- Product descriptions are used for both SEO and user experience. For faceted filter pages, the description should be brief and describe the content of the page, including the main keywords and filter applied. For example, “Shop men’s Nike athletic shoes by size, color, and style” would be a good description for the same page.
When generating title tags, H1 headings, and descriptions for faceted filter pages, don’t duplicate content across multiple pages. This is a common issue with faceted filter pages, as the same content is displayed on multiple pages with different filters applied. Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred page and avoid duplicate content.
Faceted search filter mistakes
Empty results
When offering facets based on product results and attributes, any additional selectable filters and facets should update dynamically when a user clicks on them. A good faceted search should never lead shoppers to a 0-results page and always show at least one product that matches the search criteria.
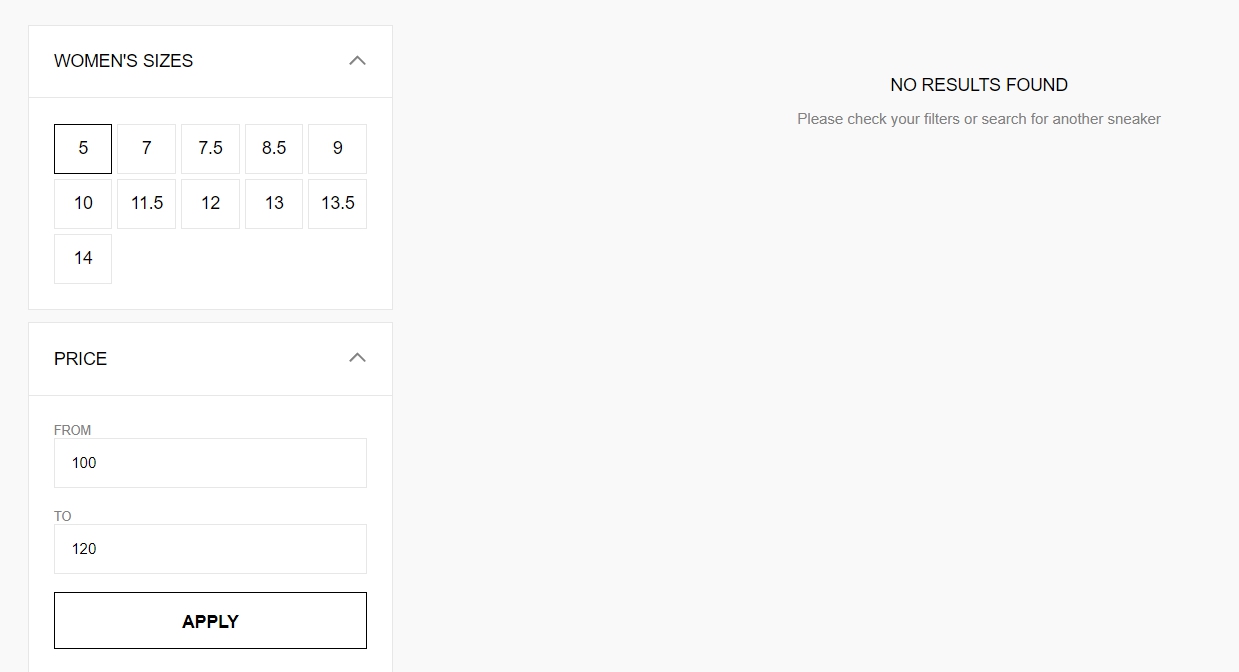
Unkind menu
Poorly designed menus cause usability issues and harm search and index quality. Here’s how to build a kind menu.
- Decide which facets are collapsible: some facets are more important than others and should always be visible, while others can be collapsed to reduce clutter on the page. Determine which facets are collapsible or expandable menus.
- Show users which facets are collapsible with icons or text.
- Use the same design for all collapsible menus across the site to provide a consistent experience. For example, use the same icon or text to indicate expandable menus everywhere.
- When a facet is collapsed, show the most popular option as the default, so users can find what they need quickly.
- Make it easy to expand and collapse menus: buttons or icons should be clear and clickable, and big enough for desktop and mobile.
- Test your collapsible menu with users and adjust.
Faceted navigation best practices
When building a faceted navigation for an e-commerce site, it’s search engine and user-friendly. Consider:
Filters
Only show filters that are relevant to your products or services. Less is more.
Product data
Product data should be consistent and standardized (product names, descriptions, prices, etc.).
Mobile faceted search
Faceted navigation should be mobile-friendly with a simple UI and filters/facets on small screens.
Store/industry facets
Show store/industry-specific facets (e.g., materials, certifications).
Reviews as a facet
Reviews as a facet (ratings).
Thematic filters
Thematic filters and facets (e.g., color, style) to group similar products/services together.
Facet order
Facet order should be based on your customers (price, brand, etc.).
Facet values
Values within each facet should be in order (alphabetical, numerical).
Selected values within facets
Show selected values within facets.
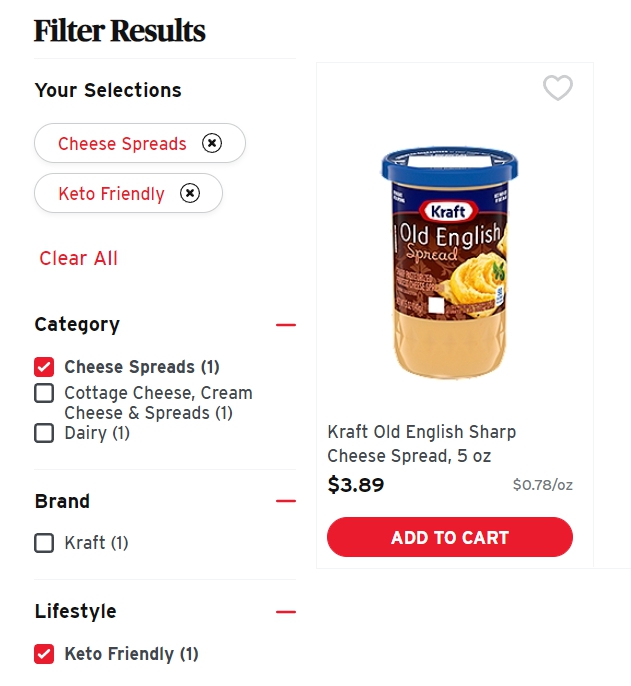
Multiple filters
Let users select multiple filters, not one at a time.
Refresh page and search results quickly
Ensure that the page and search results refresh quickly when a new filter is applied to avoid frustration and keep customers engaged.
By doing this, you’ll have a faceted navigation that’s user-friendly and helps customers find.
Conclusion
Implementing faceted search on your e-commerce website is no longer just a competitive advantage—it’s becoming an essential feature for meeting modern user expectations. As we’ve explored throughout this article, a well-designed faceted navigation system significantly enhances user experience by allowing visitors to quickly narrow down vast product catalogs to find exactly what they’re looking for.
The distinction between filters and facets is crucial to understand: filters remove items based on specific conditions, while facets group items by shared properties. When implemented together thoughtfully, they create a powerful discovery tool that can increase engagement, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction.
However, faceted search presents unique SEO challenges that require careful consideration. With potentially hundreds of thousands of filter combinations, proper indexing strategies become vital. Implementing restrictions on parameter combinations, selectively choosing which faceted pages to index, and using appropriate technical SEO tools (such as canonical tags, noindex directives, or X-Robots-Tag) can help maintain a clean and efficient site index.
For the best results, remember these key takeaways:
- Ensure your faceted navigation never leads to empty results pages
- Design mobile-friendly interfaces for your filters and facets
- Maintain consistent, standardized product data
- Organize facets in an order that matches your customers’ priorities
- Allow multiple filter selections for maximum flexibility
- Optimize performance so pages refresh quickly when filters are applied
By following these best practices, you can create a faceted search experience that not only helps users find what they need but also supports your SEO efforts and ultimately drives business growth. In the increasingly competitive e-commerce landscape, a well-implemented faceted navigation system can be the difference between a frustrated visitor who bounces and a satisfied customer who converts.

