Broken links are hyperlinks that point to non-existent pages or resources that can’t be accessed by users. When someone clicks on a broken link, they typically encounter error messages like “404 Not Found” or similar HTTP status codes instead of reaching their intended destination.
These problematic links are also known as dead links or link rot, and they occur when pages are deleted, moved, or become inaccessible for various technical reasons. Understanding what are broken links is crucial for website owners and SEO professionals, as they can significantly impact both user experience and search engine performance.
Broken links represent a common challenge in website management. They can emerge from simple typos in URLs, deleted content, or changes in website structure. As websites grow to several hundred or thousands of pages, managing broken links becomes increasingly challenging without proper checks and balances.
- Types and Examples of Broken Link Error Codes
- Common Causes and Reasons for Broken Links
- Technical Causes of Broken Links
- Why Broken Links Are Bad for SEO
- Impact on User Experience and Website Performance
- How to Find Broken Links on Your Website
- How to Fix Broken Links
- Best Practices for Broken Link Management
- FAQs
Types and Examples of Broken Link Error Codes

When users encounter broken links, they typically see various error messages that indicate different types of problems. Understanding these error codes helps identify the specific cause of broken links and determines the appropriate fix.
The most common broken link error codes include:
- 404 Not Found: The most frequent error, indicating the requested page doesn’t exist on the server
- 400 Bad Request: Occurs when the server cannot process the request due to malformed syntax
- 500 Internal Server Error: Indicates a problem with the website’s server
- 502 Bad Gateway: Shows that one server received an invalid response from another server
- 503 Service Unavailable: Means the server is temporarily unable to handle requests
- Connection Timeout: Happens when the server takes too long to respond
- Invalid Hostname: Occurs when the domain name cannot be resolved
Even a simple typo in the URL could render a link broken – a missing hyphen, an extra space, or a misspelled word can lead to a ‘page not found’ error. These seemingly small glitches can significantly harm your website’s user experience and SEO performance.
Common Causes and Reasons for Broken Links
Broken links are often created due to manual errors or website/system upgrades without proper checks and balances. Understanding the root causes helps prevent future occurrences and implement better link management practices.
The primary reasons links break include:
- Deleted or moved pages without proper redirects: When content is removed or relocated without updating internal links
- Incorrect URL formatting and typos: Manual errors when creating links, including misspelled domains or paths
- Changes in website structure or permalinks: URL modifications during site redesigns or content management system updates
- External sites going offline or changing domains: Third-party websites becoming unavailable or modifying their URL structure
- Content migration issues: Problems arising during platform transfers or website restructuring
- Domain name changes: When websites switch domains without implementing proper redirects
Website evolution is constantly driven by the need to adapt to changing technologies and user preferences, which naturally leads to structural changes that can create broken links if not managed properly.
Technical Causes of Broken Links
Beyond basic URL problems, several technical issues can cause links to break, requiring different troubleshooting approaches than simple address corrections.
Technical factors that create broken links include:
- Broken image files: When image URLs point to deleted or corrupted image files
- Malfunctioning third-party plugins: Especially social sharing buttons or embedded content widgets
- Firewall or geolocation restrictions: Security settings that prevent access from certain locations or IP addresses
- CMS plugin interference: Conflicts between content management system plugins affecting link functionality
- HTML, CSS, or JavaScript errors: Code problems that prevent proper link rendering or functionality
- Server configuration issues: Incorrect server settings that block access to specific resources
These technical issues differ from basic URL problems and require more sophisticated troubleshooting approaches, often involving developer intervention or server administration.
Why Broken Links Are Bad for SEO
Broken links impact SEO negatively simply because of poor user experience and can affect crawling, indexing, and ranking. Search engines view broken links as indicators of site quality and maintenance standards.
The SEO impact of broken links includes:
- Decreased site quality signals: Google understands that broken links are a natural occurrence but taking time to correct these issues can make a big impact on site performance
- Crawl errors preventing proper indexing: Google bots may struggle to navigate through websites with broken links, resulting in poor indexing
- Waste of link equity and page authority: Broken links prevent the flow of SEO value between pages
- Poor user experience signals: High bounce rates from broken links can negatively impact rankings
- Site maintenance perception: Search engines view broken links as a sign of poor site maintenance, which can lower the site’s ranking
While a few broken links are not likely to hurt you since most sites have some, excessive broken links can indicate site neglect and may result in algorithmic penalties.
Impact on User Experience and Website Performance
Broken links disrupt the user experience by leading users to dead ends, causing frustration and reduced trust. The cumulative effect can significantly impact business outcomes and customer relationships.
User experience consequences include:
- User frustration and confusion: Visitors encountering error pages may lose confidence in the website
- Increased bounce rates: Studies show that 89% of consumers will shop with a competitor after having a poor user experience
- Reduced conversions: Broken links prevent users from completing desired actions like purchases or sign-ups
- Damaged site reputation: Users may associate your website or brand with the frustration of encountering a broken link
- Lost return visitors: Poor experiences discourage users from returning to the site
Users expect seamless navigation, and encountering a broken link can deter them from returning to the site, ultimately affecting long-term business success and customer loyalty.
How to Find Broken Links on Your Website

Detecting broken links requires a systematic approach using various tools and methods. While Google now alerts you when users encounter inaccessible URLs, relying solely on these notifications means you’re always playing catch-up.
Effective methods for broken link detection include:
- Automated SEO crawler tools: Comprehensive site analysis tools that scan entire websites
- Google Search Console monitoring: Free tool for identifying crawl errors and indexing issues
- Specialized broken link checker tools: Dedicated software for link validation
- Browser extensions: Real-time link checking while browsing your site
- Manual review processes: Systematic clicking through important pages and links
- Regular site audits: Scheduled comprehensive website health checks
The best way to combat broken links is to prevent them from occurring at all with regular checkups – ideally checking your website for broken links at least once a quarter. For frequently updated sites, monthly checks may be more appropriate.
Professional SEO tools like Rush Analytics’ Site Audit can help automate this process, providing comprehensive broken link detection alongside other technical SEO analysis. These tools can scan thousands of pages efficiently and prioritize issues based on their impact.
Using Google Search Console for Broken Link Detection
Google Search Console is a powerful, free tool that can help identify and fix broken links on a website by providing valuable insights into site performance.
To use Google Search Console for broken link detection:
- Set up and verify your website: Add your site to Google Search Console and complete the verification process
- Navigate to the Pages report: Go to Indexing > Pages in the left sidebar
- Check the “Page indexing” section: Look for 404 errors and other crawl issues
- Review excluded pages: Examine pages that Google couldn’t index due to errors
- Monitor the “Why pages aren’t indexed” section: Identify specific problems affecting page accessibility
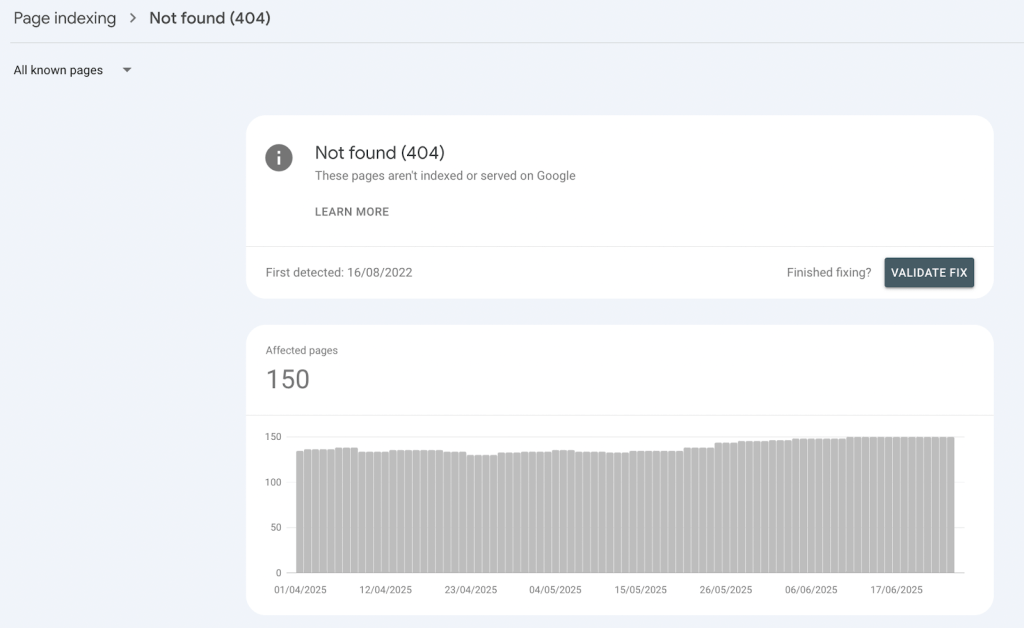
Google Search Console shows broken inbound links, which are links towards a page on your website, but it has limitations. The tool focuses on pages Google attempts to crawl rather than all links on your site.
SEO Tools and Browser Extensions for Link Checking
Various specialized tools offer more comprehensive broken link detection capabilities than Google Search Console alone.
Popular options include:
- SEO crawler tools: Platforms like Screaming Frog, Semrush Site Audit, and Rush Analytics Site Audit
- Browser extensions: Check My Links, Broken Link Checker, and similar real-time tools
- Dedicated broken link checkers: W3C Link Checker and specialized online tools
- Automated monitoring services: Tools that continuously watch for new broken links
Tools like Semonto check all links on your website, irrespective of whether they are linking to another page on your own website or to external websites, providing more comprehensive coverage than Google Search Console.
The advantage of automated monitoring is speed and coverage – these tools can scan thousands of links in minutes and provide detailed reports for efficient issue resolution.
How to Fix Broken Links
Once you’ve identified broken links, the repair strategy depends on the specific situation and the type of link involved. Common solutions include updating the URL if possible, setting a 301 redirect, or removing the link altogether if there’s no alternative.
Primary strategies for fixing broken links:
- Update URLs for moved content: Correct the link to point to the new location
- Implement 301 redirects: Redirect old URLs to relevant new pages permanently
- Remove dead links entirely: Delete links that no longer serve a purpose
- Recreate missing content: Restore deleted pages if they had value
- Replace with alternative resources: Find similar content to link to instead
- Leave as proper 404 errors: Sometimes the best solution is a well-designed error page
The decision-making criteria for choosing the appropriate fix should be based on link importance, available alternatives, and user intent. Consider the value the original link provided and choose solutions that maintain user experience while preserving SEO value.
Fixing Broken Internal Links
Internal broken links require immediate attention since they’re completely within your control and can significantly impact site navigation and SEO performance.
Strategies for internal broken links:
- Correct URL typos: Fix spelling errors or formatting mistakes in link addresses
- Republish or recreate deleted content: Restore valuable pages that were accidentally removed
- Implement 301 redirects: Redirect old URLs to relevant new pages permanently
- Update navigation menus: Ensure all menu items point to active pages
- Fix image links: Replace broken image URLs with working alternatives
- Remove outdated links: Delete links to content that’s no longer relevant
When you delete or move a webpage without updating its internal links, it creates internal broken links that are particularly harmful because they interfere with user experience and negatively impact search engine tracking.
Tools like the Wayback Machine can help recover lost content, and systematic link audits can prevent these issues from accumulating over time.
Platform-Specific Redirect Solutions
Different website platforms offer various methods for implementing redirects, each with its own advantages and technical requirements.
WordPress Solutions:
- Plugin-based redirects: Simple 301 Redirects, Redirection, or Yoast SEO plugins
- .htaccess method: Direct server-level redirects for advanced users
- WordPress admin redirects: Built-in redirect functionality in some themes
Wix Platform:
- Built-in redirect manager: Easy-to-use interface in the Wix dashboard
- Automatic redirects: Some redirects are handled automatically during site changes
- Custom redirect rules: Advanced options for complex redirect scenarios
Shopify E-commerce:
- URL redirect functionality: Built-in redirect management in admin panel
- Bulk redirect tools: Handle multiple redirects simultaneously
- Product-specific redirects: Special handling for discontinued products
When implementing redirects, be cautious about .htaccess errors and always backup your site before making changes. Test redirects thoroughly to ensure they work correctly and don’t create redirect chains.
Fixing Broken External Links and Backlinks
External link issues require different approaches since you don’t control the destination websites. External broken links are links pointing from your website to another website, which end up on pages that don’t exist due to factors beyond your control.
Strategies for external broken links:
- Find replacement sources: Locate alternative websites with similar content
- Update links to moved content: Research if the content moved to a new URL
- Remove outdated external references: Delete links that no longer provide value
- Contact site owners: Reach out to inform them of broken links
- Use archived versions: Link to Wayback Machine copies when appropriate
For broken backlinks (external sites linking to your content):
- Identify broken backlinks: Use tools like Ahrefs or Semrush to find them
- Contact linking websites: Request they update links to your current URLs
- Provide updated information: Make it easy for others to fix their links
- Monitor backlink health: Regular audits of your backlink profile
Broken backlinks represent missed opportunities and can harm your credibility and trustworthiness in the eyes of search engines, making their recovery a priority for SEO success.
Best Practices for Broken Link Management
Links will inevitably break, so it’s important to set aside time to locate and address them regularly. Implementing systematic processes prevents broken links from accumulating and causing significant problems.
Effective broken link management practices:
- Regular site audits: Schedule quarterly or monthly comprehensive link checks
- Careful content management: Plan redirects before deleting or moving pages
- Link monitoring systems: Use automated tools to detect new broken links quickly
- Deep linking strategy: Avoid linking too deeply into external sites when possible
- Content inventory maintenance: Keep track of all published content and its URLs
- Team training: Educate content creators about proper link management
- Quality assurance processes: Include link checking in content publication workflows
If you publish frequently or make changes to your website throughout the week, then monthly checks may be a better cadence to stay on top of potential issues.
Prioritization should focus on high-traffic pages, important conversion paths, and links that provide significant SEO value. Use analytics data to identify which broken links have the greatest impact on user experience and business objectives.
FAQs
What is meant by broken link?
A broken link is a hyperlink on a webpage that no longer works because the destination page has been moved, deleted, or renamed. Users clicking broken links typically see error messages instead of intended content.How do you fix broken links?
Fix broken links by updating URLs to correct locations, implementing 301 redirects to relevant pages, removing dead links entirely, or recreating valuable deleted content. Choose the method based on the specific situation and user needs.What happens if a link is broken?
When a user clicks on a broken link, they are usually redirected to an error page, which can negatively impact user experience and SEO. This can increase bounce rates and reduce site credibility.How do you identify broken links?
Use Google Search Console’s Pages report, SEO crawler tools, browser extensions, or manual checking. Automated tools like Rush Analytics Site Audit can scan thousands of links efficiently and provide detailed reports.What does a broken link look like?
Broken links typically display error messages like “404 Not Found,” “Page Not Found,” or similar HTTP status codes. They may also show blank pages or redirect to generic error pages.How to redirect broken links?
Use 301 redirects to permanently redirect broken URLs to relevant new pages. Implementation methods vary by platform – WordPress uses plugins or .htaccess, while Wix and Shopify have built-in redirect management tools.






