A product positioning map is an ideal way to understand the location of your brand or product. It also forces you to consider attributes that are important to customers and identify open areas in markets.
What is a positioning map?
A positioning map is a graph used by market researchers and companies to describe and understand the panorama of a brand or product in relation to the competition from the customer’s perspective.
In other words, a positioning map helps visualize what alternatives customers have for a particular product or brand. This chart shows the X and Y axes to talk about the qualities to be compared between a company and its respective competitors.
This chart is a great support for easily identifying the best features of a product or brand as well as its capabilities. Its greatest attribute is that it is done from the customer’s perspective, which provides greater objectivity compared to the company’s vision.
As we mentioned, a positioning map can be specifically for a product or brand. Although creation, concept and function are similar, both have different characteristics, which we mention below.
Goals of the positioning map
The main purpose of creating a positioning map is to find out how the company is positioned (in relation to its competitors) in the minds of customers.
This information is the key to:
- Find niches in the marketplace
- Develop strategies to outperform your competitor
- Learn from competitors’ strategies
- Reposition the brand in the marketplace
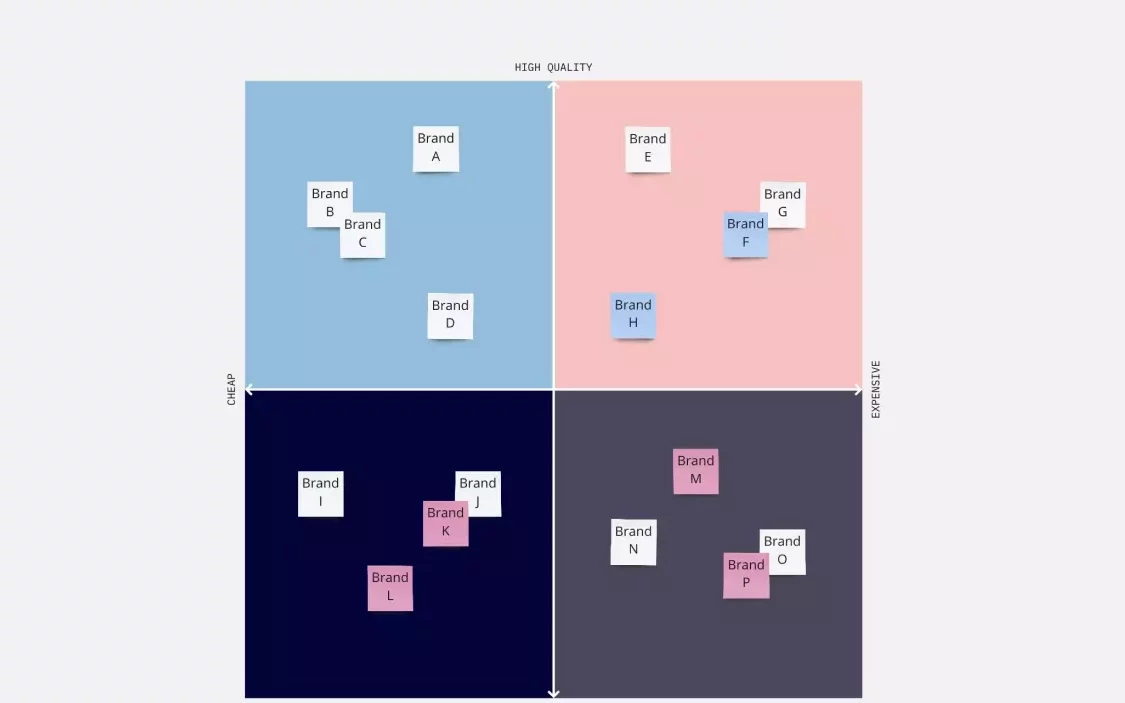
Three elements of the positioning map
1. Format
The positioning map consists of two axes (vertical and horizontal) which intersect at the ends of which you place the minimum and maximum values of each parameter you want to analyze. We will explain the steps for its development later.
2. Attributes
Remember that the attributes of the product you are going to choose must be relevant to the target market, that is, the consumers who use these attributes of your product. You have to have them as parameters to understand the differences between brands.
3. Values
Every element of the product should be recognized more or less in relation to the competition. You can create more than one perception map using multiple sets of attributes. This will help you gain more insight into the market and your environment.
How do I create a positioning map?
1. On a sheet of paper, draw 2 axes (X and Y) in the shape of a cross.
2. Assign an attribute to each axis, for example:
- X-axis: quality
- Y-axis: price
3. Each item of each axis is assigned a sub attribute of maximum value and minimum value, for example:
- X axis, right tip: high quality
- X axis, left tip: low quality
- Y axis, top tip: high quality
- Y-axis, bottom handpiece: low price
4. At this point it is observed that there are 4 quadrants:
- X right with top Y: high quality and high price
- Right X with lower Y: high quality and low price
- Left X with lower Y: low quality with low price
- Left X with top Y: low quality with high price
5. Then, based on the information you have about customer perception, the company is placed in the quadrant and at the most appropriate moment.
6. Finally, the competitors are placed.
In this way, an overview and visual panorama is obtained about the positioning of all companies in the face of consumer perception.
One of the most important aspects to consider when making a positioning map is the choice of attributes and their assignment to the axes. These attributes can be for example: quality, price, ease of use, design, usefulness, attractiveness and others. It all depends on the nature of each company, brand or product to be compared.
The benefits of a perception positioning map
Creating a positioning map allows companies to:
- Better understand what consumers think
- Know how the target market perceives the company
- Find out if the company is adapting to the market
- Evaluate the effectiveness of recent positioning campaigns
- See if the product or service really has a place in a market that may already be saturated with offers and little demand
- Maintain ongoing monitoring of the commercial introduction of new products
- Identify new preferences on the part of consumers
Disadvantages of the positioning matrix
The positioning map is a very useful tool, but its use has some limitations, such as:
- Only 2 attributes (X-axis and Y-axis) can be tested at a time. This is not very useful because purchase decisions are usually influenced by more than 2 factors.
- The perception map is usually more useful for individual brands rather than large corporate brands, where the impact on consumers is more abstract.
- Obtaining customer perception data to be able to position brands in the matrix is usually expensive. It requires market research.
- Sometimes the reality of customer perception is different from what is embodied in the positioning matrix.
Conclusion
Positioning maps are the order of the day and a very effective business analysis tool that we should not ignore. We should strive more and more for an in-depth analysis of a number of variables, improving and diversifying the way we measure, monitor and monitor the perception of our brand or product.
This will give us a more objective and contrasting view of results, because what characterizes the current market is an overabundance of information and a wide range of opinions (knowledgeable or not) about the value of a brand or product.
FAQ
What is a competitive positioning map?
▷ A positioning map is a diagram that allows you to compare your product to the competition and identify opportunities for new products in the marketplace. A positioning map plots two key product benefits on horizontal and vertical axes of a graph. These product benefits are based on what is important to the consumer.
How do you make a competitive positioning map?
- Pick two parameters. The first step is to decide on your two parameters.
- List your competitors. The next step is to list all your major competitors that offer similar products to you.
- Rate your competitors.
- Complete your perceptual mapping template.
What are the 4 competitive positions?
The four broad positions that brands typically take in the market are market leaders, market challengers, market followers, and market nichers. Depending on your broad brand position, your competitive attacks are likely to vary.

