You’ve probably noticed your website rankings fluctuating more than ever, despite following traditional SEO practices. You optimize keywords, build backlinks, and create quality content, yet your competitors seem to outrank you effortlessly. Here’s the thing: you’re still fighting yesterday’s SEO battle while search engines have moved to entity-based understanding.
If you’ve ever felt confused about why your perfectly optimized content isn’t ranking, you’re not alone. Google SEO entities represent the future of SEO—and once you understand them, everything starts making sense. These distinct concepts, people, places, and things form the backbone of how search engines like Google understand and rank content today. When you master entity SEO, you’re not just optimizing for keywords—you’re optimizing for meaning, context, and relationships that search engines use to determine relevance.
Google’s shift toward semantic search through Google’s Knowledge Graph has fundamentally changed how search engine algorithms process information. Think of it this way: instead of matching exact keywords like a simple word processor, search engines now analyze entities and their interconnections to deliver relevant search results. This means your SEO strategy must evolve beyond traditional keyword research to embrace entity identification and optimization.
Here’s what you’ll discover in this guide: practical strategies for entity research, content optimization techniques that work with Google’s natural language processing, and proven methods to measure your success. Most importantly, you’ll understand how to integrate entity-based SEO into your existing SEO work without completely overhauling your current approach.
- What Are Entities in SEO?
- The Evolution from Keywords to Entities
- Entities vs Keywords: Understanding the Key Differences
- How Google’s Knowledge Graph Powers Entity Recognition
- How Google Detects and Processes Entities
- Entity Relationships and SEO Impact
- Practical Strategies for Entity-Based SEO
- Schema Markup and Structured Data for Entities
- Essential Tools and Measurement for Entity SEO
- Advanced Entity Strategies and Future Trends
- Frequently Asked Questions About Entity SEO
What Are Entities in SEO?
Let’s break this down in simple terms. Think of entities as the building blocks of meaning in search engines. When you write about “Apple,” you’re not just using a keyword—you’re referencing a specific entity that could represent the technology company, the fruit, or even Apple Records. Entity SEO focuses on these distinct, unique concepts that search engines can recognize and understand the context through advanced processing.
An entity in SEO represents any singular concept that has unique characteristics and can be clearly distinguished from other things. These include:
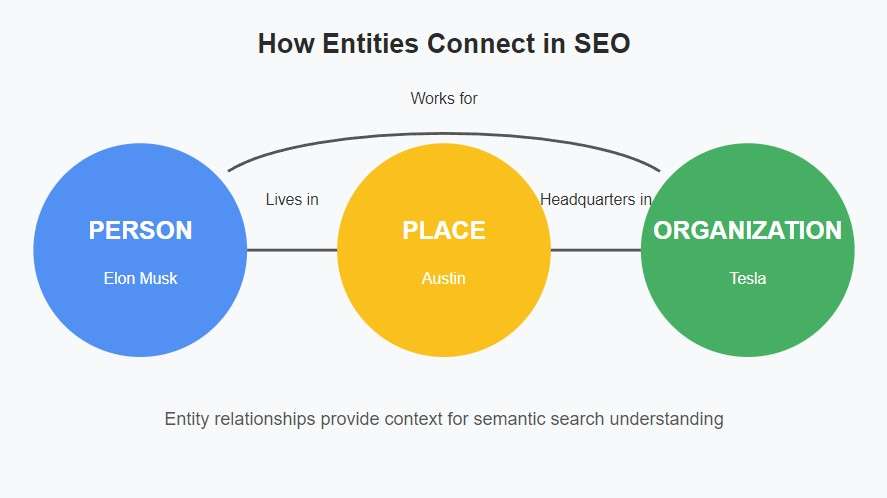
- People like “Elon Musk” or “Marie Curie”
- Places like “New York City” or “Mount Everest”
- Organizations like “Microsoft” or “World Health Organization”
- Events like “2026 Olympics” or “Black Friday”
Here’s how it works: search engines understand entities in search through named entity recognition, a natural language processing technique that identifies and categorizes these concepts within text. When you mention specific entities, you provide context that allows search engines to determine what your content is truly about, moving beyond simple keyword matching to semantic understanding.
The beauty of entities lies in their ability to provide context. If you write about “bank,” the surrounding entities help determine whether you’re discussing financial institutions, river banks, or memory banks in computers. Entities provide the contextual framework that makes modern search so accurate and relevant to user intent.
The Evolution from Keywords to Entities
You’ve witnessed SEO transform dramatically over the past decade, and if you’ve been doing this for a while, you’ll remember when you could rank by stuffing keywords into content. Those days ended when Google introduced algorithm updates that prioritized user intent over keyword density. This evolution reflects a fundamental shift from keyword-based to entity-based search understanding.
The journey began with Google Hummingbird in 2026, which enabled the search engine to understand conversational queries and focus on the intent behind user searches rather than individual keywords. RankBrain followed in 2026, introducing machine learning that helped Google interpret previously unseen search queries by understanding entity relationships. BERT in 2026 brought sophisticated natural language processing, allowing Google to grasp context and nuance in both search queries and web content.
These updates revealed the limitations of traditional keyword research. When you optimize only for specific keyword phrases, you miss the broader context that users actually seek when searching for information. Entity-based SEO solves the ambiguity problem that keyword matching cannot address. Google uses entity relationships to understand what users really want, regardless of the specific words they use.
Entities vs Keywords: Understanding the Key Differences
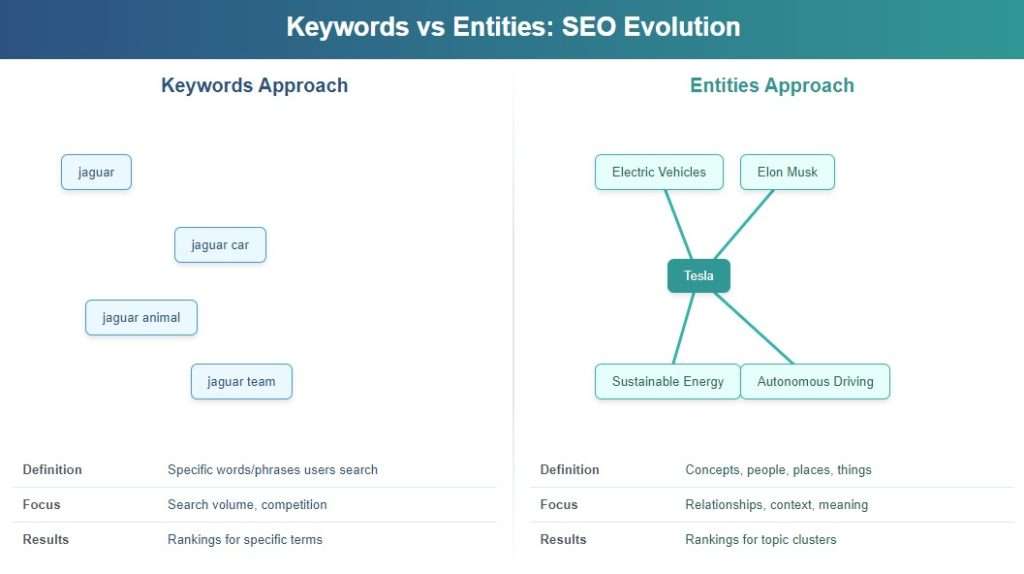
You might wonder how entities differ from the keywords you’ve been optimizing for years—and it’s a great question. While keywords are specific words or phrases users type into search engines, entities represent the actual concepts, people, places, or things those keywords refer to. This distinction fundamentally changes how you approach content optimization.
| Aspect | Keywords | Entities |
| Definition | Specific words/phrases users search | Concepts, people, places, things |
| Focus | Search volume, competition | Relationships, context, meaning |
| Strategy | Individual keyword targeting | Semantic cluster optimization |
| Results | Rankings for specific terms | Rankings for topic clusters |
| Measurement | Keyword position tracking | Semantic relevance signals |
Here’s a practical example: consider the search term “jaguar.” As a keyword, it’s simply a six-letter word. As an entity, it could reference the luxury car manufacturer, the large cat species, the operating system, or even the NFL team. Each represents a separate entity requiring completely different content strategies, even though they share the same primary keyword.
When you target the entity “Tesla” (the company), you’ll naturally include related entities like electric vehicles, Elon Musk, autonomous driving technology, and sustainable energy. This relationship approach transforms your content strategy, often resulting in better rankings for multiple relevant search queries without keyword stuffing.
How Google’s Knowledge Graph Powers Entity Recognition
Let’s dive into something fascinating: Google’s Knowledge Graph serves as the foundation for entity-based search, containing billions of interconnected entities and their relationships. When you understand how this massive database works, you can optimize your content to align with Google’s entity recognition systems effectively and understand how entities play a crucial role in modern search.
Think of the Knowledge Graph as a comprehensive encyclopedia of entities, storing information about their attributes, relationships, and contextual connections. Each entity receives a unique identifier and detailed profile that includes synonyms, related concepts, and historical information. When users search for known entities like “Barack Obama,” Google instantly accesses this database to provide rich, contextual results including related entities like “Michelle Obama,” “U.S. Presidents,” and “Democratic Party.”
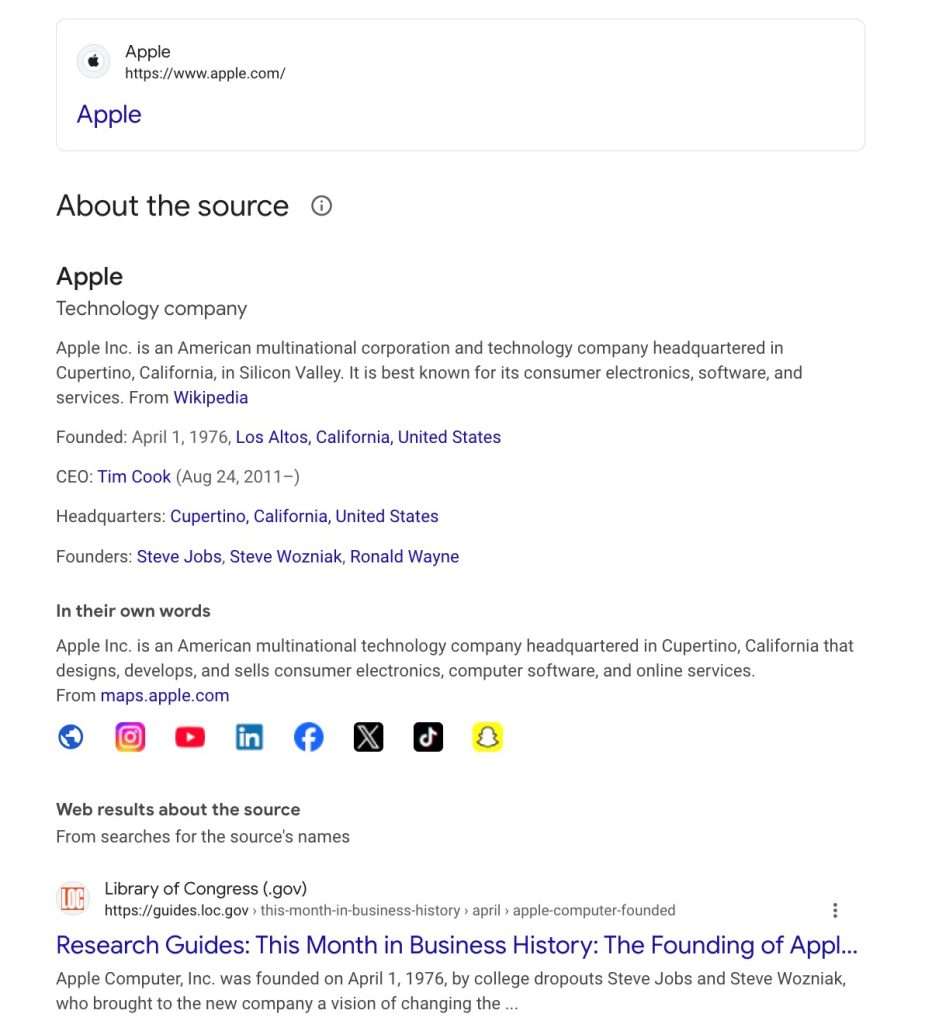
This interconnected structure enables Google to understand entity relationships at scale. Google knows that “iPhone” relates to “Apple Inc.,” which connects to “Tim Cook,” which links to “technology industry.” These relationship chains help Google determine content relevance and authority within specific topic areas, allowing it to deliver more relevant content to users.
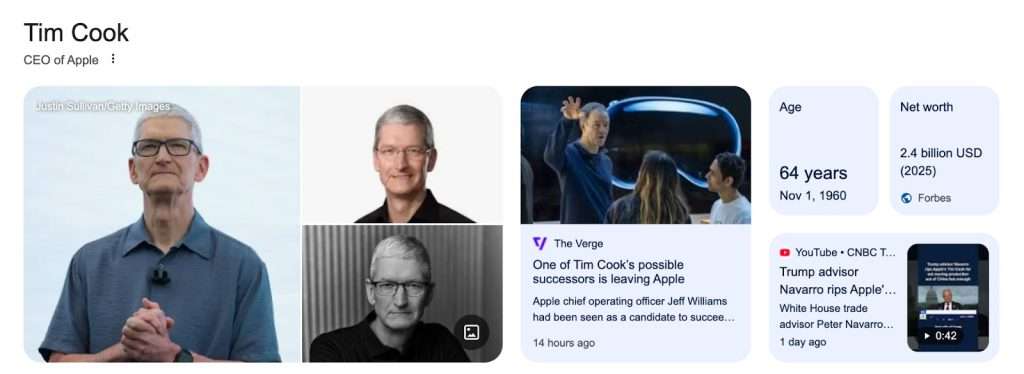
Knowledge Panels represent the most visible manifestation of entity recognition—you’ve probably seen these information boxes when searching for famous people or companies. When you search for established entities, these panels display comprehensive information sourced from the Knowledge Graph. They include images, facts, related entities, and direct answers to common questions. Earning inclusion in Knowledge Panels signals strong entity recognition and typically correlates with improved organic rankings.
The data sources feeding Google’s Knowledge Graph include Wikipedia and Wikidata, official websites, and other authoritative sources. This means establishing your brand or expertise as a recognized entity requires building presence across these platforms and earning citations from trusted sources. Understanding these interconnected entities helps you create content that aligns with Google’s semantic understanding of your industry.
How Google Detects and Processes Entities
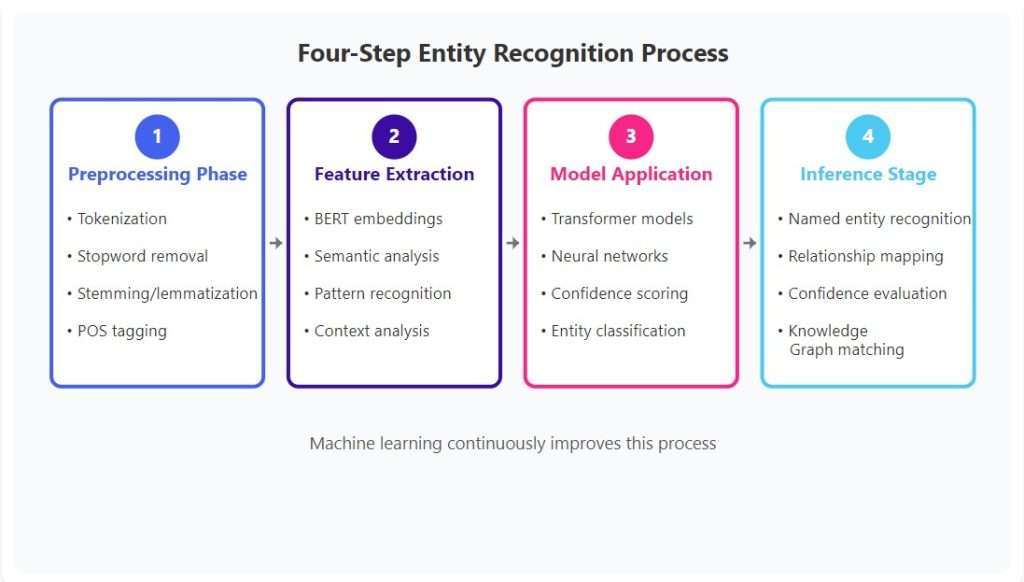
You need to understand the technical process behind entity recognition to optimize effectively—but don’t worry, we’ll break it down in digestible steps. Google employs sophisticated natural language processing and named entity recognition systems to identify and categorize entities within your content. This four-step process determines how well search engines understand your content’s meaning based on entities.
1. Preprocessing Phase: Text preparation for analysis
- Tokenization breaks content into words and phrases
- Stopword removal eliminates common but non-informative words
- Stemming and lemmatization identify root word forms
- Part-of-speech tagging assigns grammatical roles
2. Feature Extraction: Converting text to numerical data
- BERT embeddings create contextual word representations
- Semantic analysis captures meaning beyond word matching
- Pattern recognition identifies entity indicators
- Context analysis determines entity relationships
3. Model Application: Deep learning analysis
- Transformer models process numerical representations
- Neural networks recognize entity patterns
- Confidence scoring assigns reliability ratings
- Classification assigns entity types and categories
4. Inference Stage: Final entity identification
- Named entity recognition identifies specific entities
- Relationship analysis maps entity connections
- Confidence evaluation determines recognition accuracy
- Database matching links to Knowledge Graph entries
Here’s what’s really cool: machine learning continuously improves this process. As Google Cloud processes more content, the algorithms become better at recognizing new entities and understanding complex relationships between entities, making entity optimization increasingly important for SEO success.
Entity Relationships and SEO Impact
Understanding entity relationships gives you a powerful advantage in search rankings—and it’s simpler than you might think. Search engines don’t evaluate entities in isolation; they analyze the connections, co-occurrences, and contextual associations between entities to determine content quality and search relevance. When you master these relationships, you create content that naturally ranks for broader topic clusters.
Entity relationships manifest in several ways that directly impact your SEO performance:
- Co-occurrence relationships: Important entities frequently appearing together across authoritative content
- Hierarchical relationships: Broader concepts encompassing more specific sub-entities
- Causal relationships: Entities connected through cause-and-effect associations
- Temporal relationships: Entities linked through time-based connections
- Semantic relationships: Entities sharing similar meanings or contexts
The strength of entity relationships influences ranking potential significantly. Strong relationships between highly relevant entities signal content depth and expertise. For instance, relevant content about “artificial intelligence” that naturally incorporates related entities like “machine learning,” “neural networks,” and “data science” demonstrates comprehensive understanding that search engines reward.
These connections between entities create multiple pathways to discovery. When you optimize for entity relationships, your content becomes relevant for various related search queries without explicitly targeting each keyword. This approach increases organic traffic potential while improving content efficiency and user experience.
Here’s the practical side: search engines also analyze relationship strength through link analysis, co-citation patterns, and user behavior signals. Content that successfully connects related entities through internal linking and comprehensive coverage often sees improved rankings across multiple search terms within the topic cluster.
The contextual relevance factor determines how well your entity usage matches user search intent. When you demonstrate understanding of entity relationships through natural content flow, search engines recognize your content as authoritative and comprehensive, leading to better rankings and enhanced visibility.
Practical Strategies for Entity-Based SEO
You can implement entity-based SEO through systematic approaches that integrate with your existing SEO strategy—and the best part is, you don’t need to start from scratch. These proven techniques help you identify relevant entities, optimize content effectively, and measure results accurately. Let’s start with entity research to build a foundation for your optimization efforts and learn how to use entities effectively in your digital marketing approach.
Strategy 1: Comprehensive Entity Research
Begin entity research by identifying your primary topic entities. If you’re in the fitness industry, for example, core entities might include:
- Primary entities: Strength training, cardiovascular exercise, nutrition
- Related entities: Weight loss, muscle building, athletic performance
- Supporting entities: Equipment brands, exercise techniques, dietary supplements
- Expert entities: Fitness professionals, nutritionists, sports scientists
Use Google’s Knowledge Graph API to explore entity relationships and discover connected concepts that your audience values. This systematic approach reveals entity opportunities that competitors might overlook.
Strategy 2: Competitive Entity Analysis
Here’s where it gets interesting: analyze your top competitors’ entity usage through content analysis tools. Examine which entities appear consistently across high-ranking pages in your niche. This competitive analysis reveals entity gaps in your current content and opportunities for comprehensive topic coverage that outperforms existing results.
For practical entity optimization, tools like Rush Analytics Content Optimizer make this process systematic and data-driven. The Content Optimizer analyzes your competitors’ entity usage patterns and provides specific recommendations for entity inclusion. By examining actual Google SERP results, you can identify which entities successful pages incorporate and optimize your content accordingly.
The tool shows you exactly which related entities to include and how frequently, taking the guesswork out of entity optimization. What sets Rush Analytics apart is its ability to analyze not just main content but also text fragments, anchor texts, and page titles—giving you complete entity coverage analysis. This comprehensive approach goes a long way toward improving your search performance. You can access this powerful functionality at https://rush-analytics.com/land/content-optimization-tool to streamline your entity research process.
Strategy 3: Entity-Rich Content Creation
Create entity-rich content by naturally incorporating identified entities throughout your pages. The key here is avoiding forced inclusion—instead, develop comprehensive coverage that naturally addresses related concepts. For example, a piece of content about “email marketing” should organically mention:
- Open rates and click-through performance metrics
- Segmentation strategies and audience targeting
- Automation workflows and drip campaigns
- Deliverability factors and inbox placement
- A/B testing methodologies and optimization
Strategy 4: Topical Clustering Implementation
Implement topical clustering by organizing content around entity themes. Create pillar pages that comprehensively cover primary entities, then develop supporting content that explores related sub-entities. Link these pages strategically to demonstrate entity relationships and topical authority, building strong E-E-A-T signals in the process.
Schema Markup and Structured Data for Entities
Schema markup serves as a direct communication channel between your content and search engines—think of it as giving Google a roadmap to understand your content. When you implement structured data correctly, you eliminate ambiguity about your content’s entities and significantly improve search engine understanding. Implementing schema properly allows search engines to process your content more effectively.
Entity identification through schema markup involves selecting appropriate schema types for your content entities. The process requires strategic implementation:
- Choose appropriate schema types for your entities
- Include essential entity properties like name, description, and identifiers
- Add relationship connections through sameAs and relatedLink properties
- Validate implementation using Google Search Console and testing tools
Primary entity designation helps search engines identify your page’s main focus. Use the “about” property in WebPage schema to specify your primary entity, and include “mentions” properties for related entities discussed within your content. This approach creates clear entity hierarchies that support search engine comprehension and enhance E-E-A-T signals.
Entity linking through “sameAs” properties connects your entities to authoritative sources like Wikipedia, official websites, and industry databases like Crunchbase. These connections strengthen entity recognition and establish credibility through association with trusted sources.
Example Schema Implementation:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"about": {
"@type": "Thing",
"name": "Entity SEO",
"sameAs": "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Named_entity"
},
"mentions": [
{
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Google",
"sameAs": "https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google"
}
]
}
Validation tools like Google’s Rich Results Test and Schema.org’s validator help ensure proper implementation. Regular testing prevents markup errors that could confuse search engines or prevent entity recognition from functioning correctly.
Essential Tools and Measurement for Entity SEO
Measuring entity SEO success requires specialized tools and metrics that go beyond traditional keyword tracking—but don’t worry, we’ll guide you through the essentials. You need systems that monitor entity recognition, relationship strength, and semantic relevance to evaluate your optimization efforts effectively and understand how to use entities in your broader digital marketing strategy.
Essential Entity SEO Tools
Google Cloud Natural Language Processing API provides direct insight into how Google’s algorithms interpret your content entities. This tool analyzes your text and returns identified entities with confidence scores, revealing which concepts Google recognizes most clearly. Regular analysis helps you refine content to improve entity recognition accuracy and understand user queries better.
Knowledge Graph Search API allows you to explore entity relationships and discover optimization opportunities. Query this API to understand how Google categorizes entities and their connections, then align your content strategy with these recognized relationships for improved relevance.
Content optimization platforms like Rush Analytics offer comprehensive entity analysis within their content optimization suites. These tools compare your entity usage against top-ranking competitors and provide specific recommendations for improvement. They analyze entity frequency, context, and relationships to guide your optimization decisions systematically and improve your E-E-A-T profile.
Schema markup validation tools ensure your structured data correctly identifies entities for search engines. Use Google Search Console to monitor structured data performance and identify implementation issues that might prevent proper entity recognition.
Key Performance Indicators
Success measurement focuses on several key performance indicators that reflect entity optimization effectiveness:
- Knowledge Panel appearances for your brand or expertise entities
- Improved rankings for semantically related search queries
- Increased organic traffic from long-tail, entity-related searches
- Higher click-through rates from enhanced search result features
- Better user engagement metrics indicating content relevance
- Featured snippet captures for entity-focused content
Measurement Framework
Track these metrics consistently to identify successful entity optimization strategies and areas requiring improvement:
- Entity recognition accuracy through NLP API testing
- Semantic ranking improvements for related keyword clusters
- Knowledge Graph inclusion monitoring and expansion
- User engagement signals indicating content relevance
Here’s the reality: entity SEO often shows results gradually as search engines build confidence in your content’s semantic relevance. Monitor progress over 3-6 month periods to identify meaningful trends and optimization opportunities, especially when building your Google Business Profile and social media profiles presence.
Advanced Entity Strategies and Future Trends
The future of SEO increasingly favors entity-based understanding, especially with AI-powered search experiences and large language models. Here’s what you need to know: preparing for these developments by implementing advanced entity strategies positions your content for evolving search technologies and strengthens your overall E-E-A-T strategy.
Building content knowledge graphs creates internal entity networks that demonstrate topical authority. Map your content’s entity relationships through strategic internal linking that connects related concepts naturally. For example, link mentions of “artificial intelligence” to your comprehensive AI content, and connect “machine learning” references to relevant technical guides.
Common Entity Optimization Mistakes to Avoid:
- Over-optimization through forced entity inclusion without natural context
- Neglecting entity relationships while focusing only on primary entities
- Ignoring schema markup implementation for explicit entity identification
- Creating shallow content that mentions entities without comprehensive coverage
Future search technologies will rely even more heavily on entity understanding. Large language models like GPT and Google’s LaMDA process information through entity recognition and relationship analysis. Voice search, visual search, and conversational AI all depend on sophisticated entity comprehension to deliver accurate responses.
Your preparation strategy should focus on:
- Build comprehensive entity coverage across your content ecosystem
- Establish authoritative entity recognition through consistent optimization
- Create natural entity relationships that demonstrate expertise
- Monitor algorithm updates that affect entity processing
Here’s the bottom line: focus on building genuine expertise and authority rather than attempting to manipulate algorithmic signals. Building strong Crunchbase listings and maintaining accurate business information across platforms also contributes to entity recognition. The integration of entity-based SEO with AI search represents the future of organic visibility—position your content strategy now to maintain competitive advantages.
Frequently Asked Questions About Entity SEO
What are SEO entities?
SEO entities are distinct concepts, people, places, organizations, or things that search engines can recognize and understand within content. Unlike keywords, which are specific words or phrases, entities represent the actual meaning behind those terms and understand the context of the content. For example, when you mention “Tesla,” search engines understand whether you’re referring to the electric car company, the inventor Nikola Tesla, or Tesla energy products based on contextual entities surrounding the mention. Entities provide the semantic foundation that enables modern search engines to deliver more relevant, context-aware results and improve E-E-A-T signals.How to find related entities in SEO?
You can identify related entities through several systematic approaches—and it’s easier than you might think. Start by analyzing your top competitors’ content to see which entities they consistently mention alongside your primary topic. Use Google’s “People also ask” and “Related searches” sections to discover entity connections. The Google Knowledge Graph API provides programmatic access to entity relationships, while content analysis tools can extract entities from high-ranking pages in your niche. Additionally, examine Wikipedia pages for your main entities to understand their relationship networks and explore semantic associations that enhance your content’s topical authority.Does schema markup help with entity SEO?
Absolutely! Schema markup significantly enhances entity SEO by explicitly identifying entities for search engines. When you implement structured data using schema.org vocabulary, you remove ambiguity about which entities your content discusses. This markup helps search engines understand entity attributes, relationships, and context more accurately than relying solely on natural language processing. Proper schema implementation often correlates with improved rankings and enhanced search result features like Knowledge Panels and rich snippets, creating a direct communication channel between your content and search algorithms.How can I measure entity SEO success?
Entity SEO success measurement requires tracking multiple indicators beyond traditional keyword rankings—but it’s totally manageable once you know what to look for. Monitor Knowledge Panel appearances for your brand entities, track rankings for semantically related search queries, and measure organic traffic growth from entity-related long-tail searches. Use Google’s Natural Language Processing API to assess how well Google recognizes entities in your content. Additionally, track user engagement metrics like time on page and bounce rate, as better entity optimization typically improves content relevance and user satisfaction within your broader SEO work.
Article Sources
- Google Knowledge Graph Search API Documentation
- Schema.org Structured Data Guidelines
- Google’s Natural Language Processing Research
- Google Search Central Entity Documentation
- Named Entity Recognition in Search
- Knowledge Graph and Semantic Search Studies






