After eight years of optimizing websites ranging from small local businesses to enterprise e-commerce platforms, I’ve refined these five battle-tested methods for finding internal links to any page. Each approach serves different scenarios, and knowing when to use which SEO tools can literally save your website from search engine ranking disasters.
Method 1: Dedicated Internal Link Tools (Link Whisper, LinkStorm) – Best for automated suggestions
Method 2: SEO Spiders (Screaming Frog) – Most accurate for comprehensive analysis
Method 3: Google Search Console – Free option with basic functionality
Method 4: SEO Suites (Ahrefs, Semrush) – Powerful for competitive analysis
Method 5: Manual Audits – Essential for verification and small sites
5 Effective Methods to Find Internal Links to a Page

When evaluating internal link analysis methods, I consider four critical factors: accuracy (can I trust the data?), speed (how quickly can I get results?), cost-effectiveness (what’s the ROI?), and ease of use (can my team implement this?). The methods I’m sharing have proven themselves across hundreds of client projects, helping search engines understand site structure while improving search engine results positioning.
| Method | Cost | Time Required | Accuracy | Best For |
| Dedicated Tools | $69-299/year | 5-10 minutes | Very High | WordPress sites, automation |
| SEO Spiders | $149-659/year | 15-30 minutes | Excellent | Large sites, comprehensive analysis |
| Google Search Console | Free | 10-15 minutes | Good | Quick checks, budget constraints |
| SEO Suites | $99-999/month | 10-20 minutes | Very High | Competitive analysis, enterprise |
| Manual Audit | Free | 2-8 hours | Variable | Small sites, verification |
Method 1: Using Dedicated Internal Link Tools
Specialized SEO tools like Link Whisper, LinkStorm, and Internal Link Juicer are purpose-built for one thing: making internal linking effortless. These tools excel at finding existing contextual links and suggesting new opportunities based on content analysis, while helping search engines understand the relationships between your pages.
LinkStorm, for example, uses AI-powered analysis to crawl your website and suggest relevant internal links based on semantic content analysis. What sets these tools apart is their focus on automation without sacrificing quality, analyzing different types of internal links from navigational links to contextual content connections.
Here’s my step-by-step process using Link Whisper (which I’ve used on over 200 WordPress sites):
- Install and activate the plugin from your WordPress dashboard
- Navigate to Link Whisper > Link Opportunities to see suggested internal links
- Click on any target page to view all existing internal links pointing to it
- Use the “Inbound Suggestions” tab to see which pages could link to your target page
- Export the data for further analysis in spreadsheets
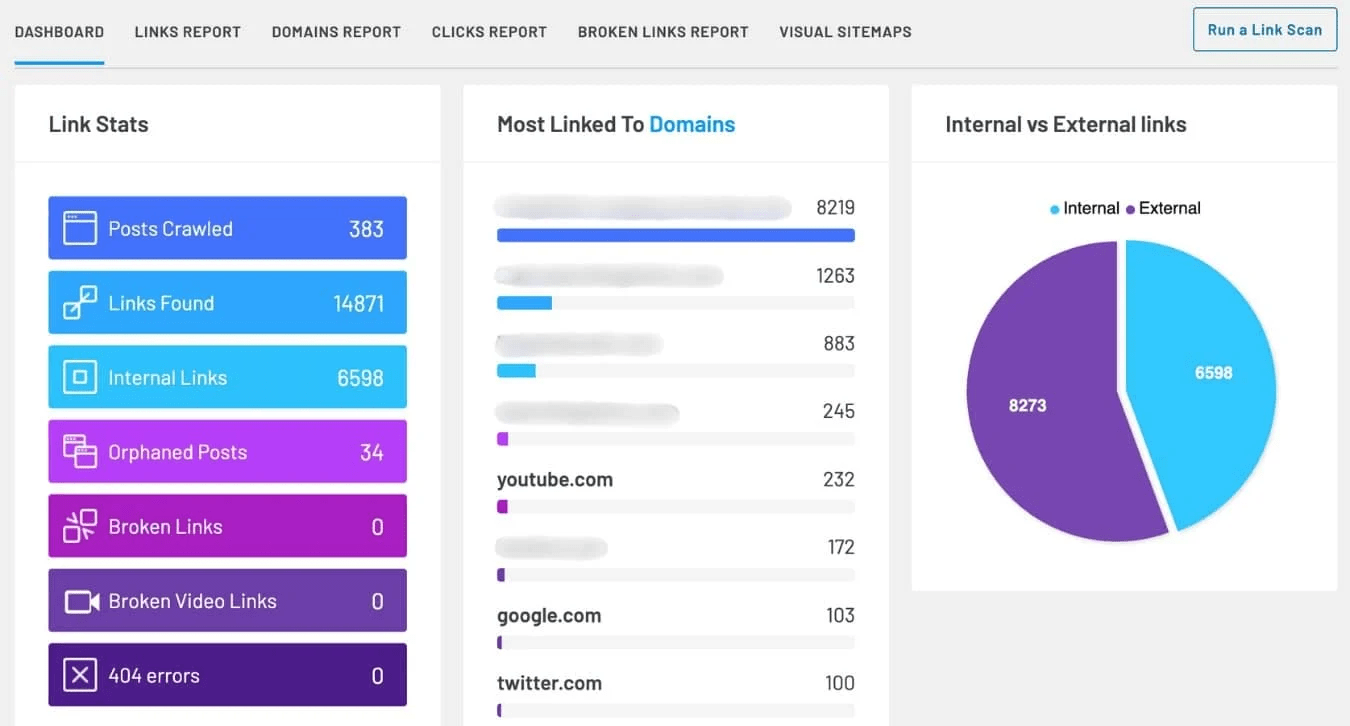
The beauty of dedicated tools lies in their contextual understanding. Rather than just matching keywords, they analyze semantic relationships between your content pieces, identifying opportunities for both navigational links and contextual links. Tools like LinkStorm can identify internal linking gaps across web pages using proprietary web crawlers that index website content into their database, helping search engines crawl and understand your site structure more effectively.
Pro tip: I always cross-reference suggestions from these tools with my content strategy. A tool might suggest linking from a high-traffic blog post to a product page, but if the context doesn’t naturally support it, I skip that suggestion to maintain user experience quality and avoid potential link schemes that search engines might penalize.
Method 2: Leveraging SEO Spiders for Internal Link Analysis
Screaming Frog SEO Spider remains my go-to tool for comprehensive internal link analysis, especially for larger websites. Its accuracy and depth of data make it indispensable for technical SEO audits, providing detailed insights into how search engine crawlers navigate your site structure.
When I need to find all internal links pointing to a specific page, here’s my exact Screaming Frog workflow:
- Launch Screaming Frog and enter your website’s homepage URL
- Start the crawl and wait for completion (can take 5-60 minutes depending on site size)
- Navigate to the “Internal” tab to see all internal links discovered
- Use the search function to filter for your target URL
- Click on the “Inlinks” tab at the bottom to see all pages linking to your target page
- Export the data using the “Bulk Export > All Inlinks” option
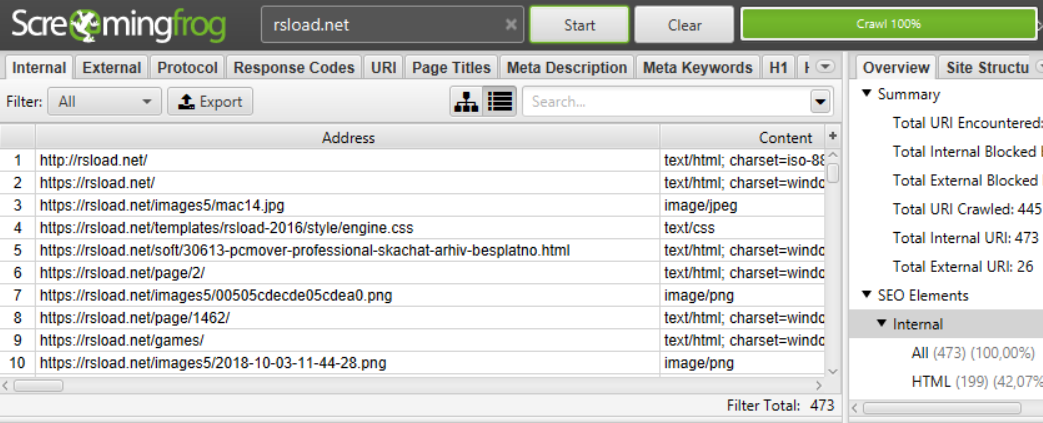
The Inlinks tab reveals crucial information: source URL, anchor text, link position, and link type (text or image). This granular data helps me understand not just where links exist, but their context and quality. You can also identify nofollow links and external links that might be affecting your site’s link equity distribution.
For larger sites exceeding 500 pages, I configure Screaming Frog with these optimized settings to ensure efficient crawling of indexed pages:
- Crawl depth limit: 5 levels maximum
- Crawl speed: Medium (to avoid server strain)
- Include external links: Disabled (to focus on internal structure)
- Store images: Disabled (to speed up crawling)
Advanced technique: I create custom filters to identify internal link patterns and potential issues. For instance, filtering by anchor text reveals over-optimization issues and helps diversify anchor text usage, while filtering by link position helps identify navigationally important links versus contextual links. This analysis also helps spot nofollow links that might be blocking link equity flow unnecessarily.
Method 3: Using Google Search Console to Check Internal Links
Google Search Console’s Links report provides free access to both external links and internal link data, consolidated from the old “Links to your site” and “Internal Links” reports. While not as comprehensive as paid SEO tools, it offers valuable insights directly from Google’s perspective on how search engines interpret your site structure.
Here’s how I use Search Console for internal link analysis:
- Log into Google Search Console and select your property
- Navigate to “Links” in the left sidebar
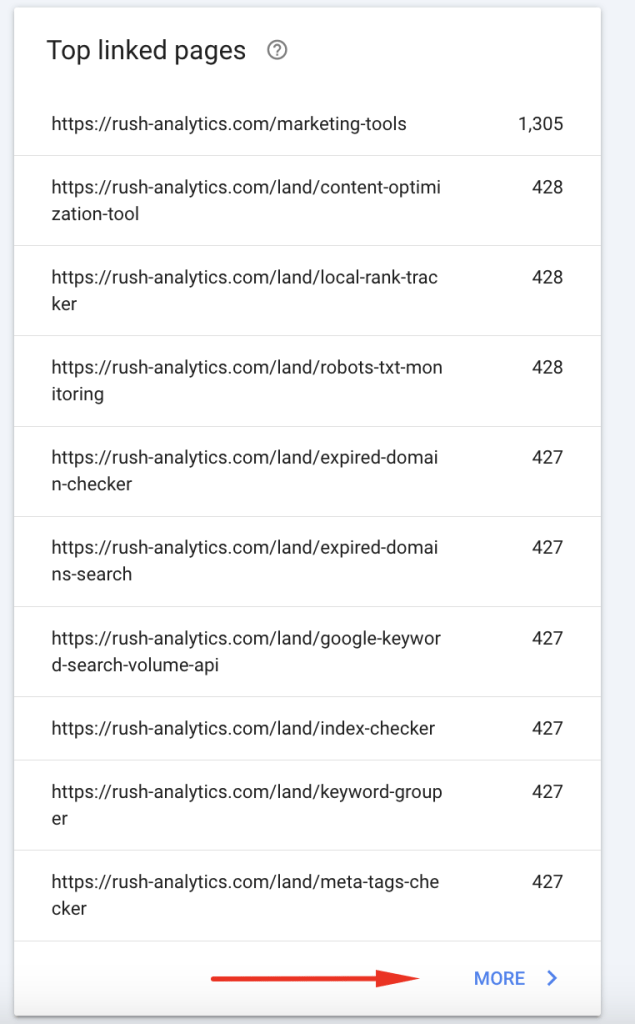
- Click on “Internal links” to see your most internally linked pages
- Select “Top linked pages” to identify pages with the most internal links
- Click “MORE” to see the complete list of internally linked pages
- Click on any specific page to see which pages link to it
The internal links report is particularly valuable for identifying pages with few internal links – I suggest going to “Links” → “Internal links” → “Top linked pages,” identifying important pages with few internal links, and adding more internal links to those pages.
Limitations I’ve encountered: Search Console’s data is sampled, meaning you won’t see every internal link or all external links. The report includes links Google has found over time, and these links may have since been removed, or indexed pages may no longer exist. Additionally, it doesn’t distinguish between nofollow links and regular links. For quick audits and budget-conscious clients, however, it provides sufficient insight to identify major internal linking gaps and understand how search engines view your site structure.
Practical application: I use Search Console to quickly identify “orphan pages” – important pages with surprisingly few internal links. These represent immediate optimization opportunities that can boost page authority and crawlability.
Method 4: Utilizing Comprehensive SEO Suites
Platforms like Ahrefs, Semrush, and Moz offer powerful internal link analysis through their site audit features, with tools like Ahrefs Site Explorer creating internal linking reports that identify the top 10 trafficked keywords for each crawled page. These SEO tools excel at combining internal link data with broader search engine optimization metrics.
My Ahrefs internal link analysis process:
- Access Site Audit in your Ahrefs dashboard
- Set up a new project for your target website
- Run a comprehensive crawl (usually takes 10-45 minutes)
- Navigate to “Internal linking” report in the Site Audit results
- Filter by the target page URL to see all linking pages
- Export data to Excel for advanced filtering and analysis
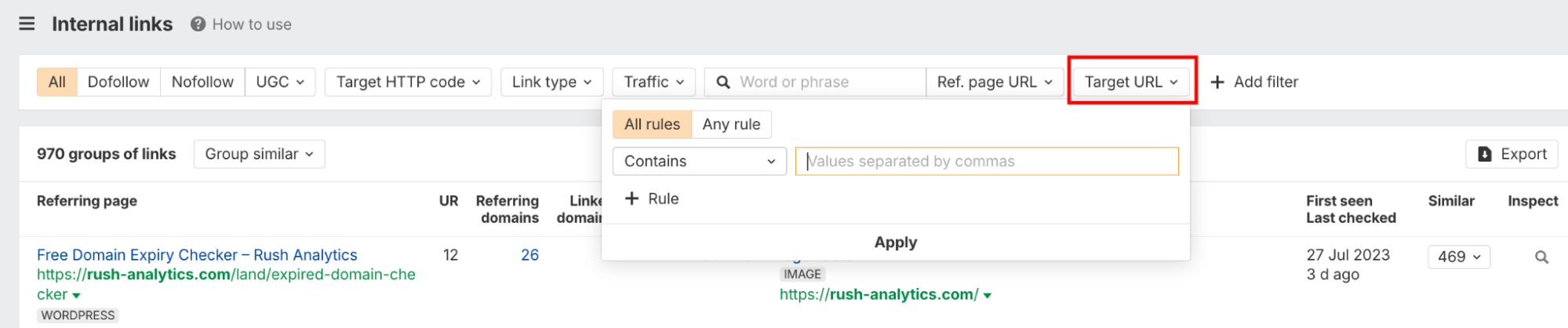
What makes SEO suites powerful is their ability to combine internal link data with other SEO metrics. You can filter results by domain rating to see which pages are your most authoritative, as any pages you link to from these high-ranking pages will enjoy a boost in link equity. The Site Explorer feature also reveals how external links and internal links work together to influence search engine rankings.
Advanced strategy: I create internal link priority matrices in Excel, combining:
- Source page authority (from Ahrefs DR)
- Target page importance (based on business objectives)
- Current link count
- Anchor text diversity and optimization potential
This data-driven approach helps prioritize which internal links will deliver the highest impact on search engine rankings while avoiding manipulative link schemes that could trigger penalties.
Method 5: Performing a Manual Internal Link Audit
Sometimes, automated tools miss nuances that only human analysis can catch. Manual audits, while time-intensive, provide the highest quality control and contextual understanding.
I resort to manual internal link checking in these scenarios:
- Small websites (under 50 pages) where manual review is efficient
- Quality verification of automated tool suggestions
- Contextual analysis to ensure link relevance and user experience
- Anchor text optimization requiring editorial judgment
My streamlined manual audit process:
Browser shortcuts I use for efficiency:
- Ctrl+F (Cmd+F on Mac): Search for target URL on each page
- Ctrl+U (Cmd+Option+U): View page source to find hidden or JavaScript-generated links
- F12: Open developer tools to inspect dynamically loaded content
- Ctrl+Shift+I: Inspect specific elements for link attributes
Manual audit checklist:
- Check main navigation menus
- Review footer links
- Scan sidebar widgets and promotional boxes
- Examine in-content contextual links
- Verify related post sections
- Inspect breadcrumb navigation
While manual audits are labor-intensive, they reveal link opportunities that automated tools often miss, such as semantically relevant but not keyword-exact matches.
Comparing the Methods: Which One Is Right for You?
After implementing these methods across hundreds of websites, I’ve developed clear guidelines for method selection based on specific scenarios.
For WordPress sites under 500 pages: I recommend Link Whisper or similar dedicated tools. The automation saves hours of manual work, and the suggestions are surprisingly accurate for content-rich sites.
For large e-commerce or enterprise websites: Screaming Frog provides the most comprehensive data. The ability to export detailed link reports and cross-reference with other technical SEO issues makes it indispensable for complex sites.
For budget-conscious small businesses: Start with Google Search Console’s free internal links report. While limited, it identifies the biggest opportunities without additional cost.
| Factor | Dedicated Tools | SEO Spiders | Search Console | SEO Suites | Manual Audit |
| Accuracy | Very High | Excellent | Good | Very High | Variable |
| Speed | Fast | Medium | Fast | Medium | Very Slow |
| Cost | Low-Medium | Medium | Free | High | Free |
| Learning Curve | Easy | Medium | Easy | Medium | Easy |
| Data Depth | High | Excellent | Basic | Excellent | High |
My professional recommendation: Use a combination approach. Start with Google Search Console for quick wins, then dive deeper with either dedicated tools (for content sites) or SEO spiders (for technical sites) for comprehensive analysis.
Free 7 days access to all tools. No credit card required!
Попробовать бесплатно
Why Finding Internal Links Matters for Your SEO Strategy
Understanding your internal link structure isn’t just about counting links – it’s about optimizing the flow of authority and user experience throughout your website. Internal linking helps search engines discover pages on your site and helps users navigate to different pages, while also distributing link equity across your site structure. Search engines understand your content hierarchy better when internal links create clear pathways between related topics.

The five critical reasons why internal link analysis drives SEO success:
- Authority distribution: Internal links pass ranking power from high-authority pages to important but less-linked pages, influencing search engine rankings
- Crawl efficiency: Search engine crawlers use internal links as pathways to discover and understand your site’s content hierarchy
- User engagement: Strategic contextual links reduce bounce rates and increase pages per session
- Topic clustering: Related internal links help establish topical authority in your niche, signaling expertise to search engines
- Conversion optimization: Well-placed navigational links and contextual links guide users toward conversion pages
Common Scenarios When You Need to Find Internal Links
Through my consulting experience, I’ve identified specific situations where internal link analysis becomes mission-critical:
Website migrations and URL changes: When restructuring your site, identifying all internal links prevents broken link disasters. I recently helped a client migrate from HTTP to HTTPS – finding 847 internal links pointing to old HTTP URLs that needed updating.
Content consolidation projects: Merging or redirecting old content requires knowing exactly which pages link to your target URLs. For businesses with multiple locations and different landing page URLs, analyzing internal link distribution can reveal why some locations rank better than others.
Broken link cleanup: 404 errors create poor user experience and waste link equity. Regular internal link audits help identify and fix broken internal links before they impact your SEO performance.
Critical scenarios requiring immediate internal link analysis:
- Post-migration SEO drops – Traffic decreases after site changes
- New page launch – Ensuring important pages get proper internal link support
- Content pruning – Before deleting pages, redirect their link equity
- Technical SEO audits – Comprehensive site health assessments
- Competitor gap analysis – Understanding internal linking strategies in your niche
What to Do After Finding Your Internal Links
Discovering your internal link structure is only the first step. The real SEO value comes from optimizing what you find.
Immediate actions I take after internal link analysis:
Fix structural issues: Look for pages with zero internal links (orphan pages) and connect them to your site’s navigation structure. Add relevant internal links from high-authority pages to distribute link equity effectively, ensuring search engines can discover all indexed pages.
Optimize anchor text diversity: Avoid over-optimization by using varied, descriptive anchor text. Instead of linking with “SEO services” repeatedly, use variations like “search engine optimization,” “SEO consulting,” and “organic search strategies.” This natural anchor text variation helps search engines understand context without triggering spam filters.
Address link equity flow: Identify high-authority pages (often your homepage or popular blog posts) and ensure they link strategically to your most important pages. Add contextual links from pages that have the most external links pointing to them, as these typically pass the most authority and can significantly impact search engine results positioning.
FAQs
How to find internal links on a page?
Use your browser’s search function (Ctrl+F) to search for your target URL on each page, or use tools like Screaming Frog to crawl your entire site and filter for specific internal links.How to find internal URL?
Internal URLs are links pointing to pages within your same domain. You can identify them using Google Search Console’s internal links report or SEO crawler tools like Screaming Frog.How do I find a page that links to a specific URL?
Check Google Search Console’s Links report under “Internal links,” use Screaming Frog’s Inlinks tab, or search your site’s HTML source code for the target URL using browser developer tools.How to track internal link clicks?
Set up Google Analytics event tracking for internal links using Google Tag Manager, or use heatmap tools like Hotjar to visualize which internal links users click most frequently.How can we find all the links on a web page?
Use browser developer tools (F12), view page source (Ctrl+U), or employ SEO crawler tools like Screaming Frog to extract all links from a specific page, both internal and external.






