If you run a website, you know how important it is to keep your content fresh. Crawlable pages are essential for good search rankings and organic traffic. Search engines use bots to find and index pages based on the user’s intent and searches. If pages are not crawlable they won’t show up in search results.
What does it mean the page is crawlable?
For a page to be crawlable means search engine crawlers or spiders can fully access and scan the content to understand the search intent behind the page. The bots should be able to access the full HTML content without any barriers like login requirements or robots.txt restrictions.
Once accessed, the crawler scans the page content, extracting information from the text, tags, links, and page structure. It analyzes this data to determine the topic and intent of the page and how well it matches search queries. Making your content crawlable allows search engines to properly index your pages and assess them for various search intents as part of your overall SEO strategy. It ensures your target audience can find your site for relevant searches.
Here you can check if your page or entire site is indexed by Google
Why does it matter?
Search engines need to crawl your pages to index them. If a page can’t be crawled, it won’t be indexed. If search engines can’t crawl a page, it won’t show in search results, even if the content is awesome. Crawlability is SEO. It’s the first step to getting pages indexed so they can rank and be found by your people through search. If a page isn’t crawlable, it won’t show in results and won’t get organic traffic.
Crawlability vs. indexability
Crawlability is when search bots can access your pages, and indexability is when those pages show in search results. Website crawlability is whether a search engine can access and read your pages. Indexability for search terms is whether the search engine includes those pages in its index.
A page can be crawled but not indexed if it has duplicate content or noindex tags. A page that can’t be crawled won’t be indexed. Pages must be crawlable before they can be indexed and ranking for keywords and search intent.
How to check if the page is crawlable and indexable?
Method one, the most simple: Google Search Console
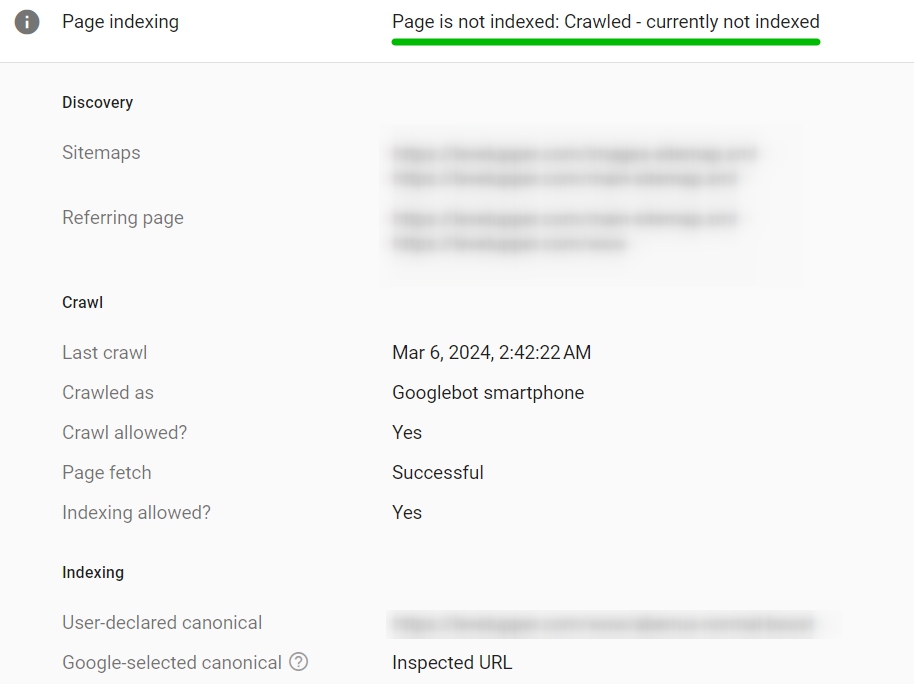
One of the quickest ways to see if a page is crawlable and indexable is to use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console. That’s where website owners can see their site in Google search results. To check if a site or page is crawlable and indexable, log in to your Google Search Console account, go to the URL Inspection Tool and enter the page URL. It’ll show if it’s been crawled and indexed and why—crawl errors or robots.txt blockages, for example. These show what you need to fix to improve search engine visibility.
Method two: Screaming Frog SEO Spider
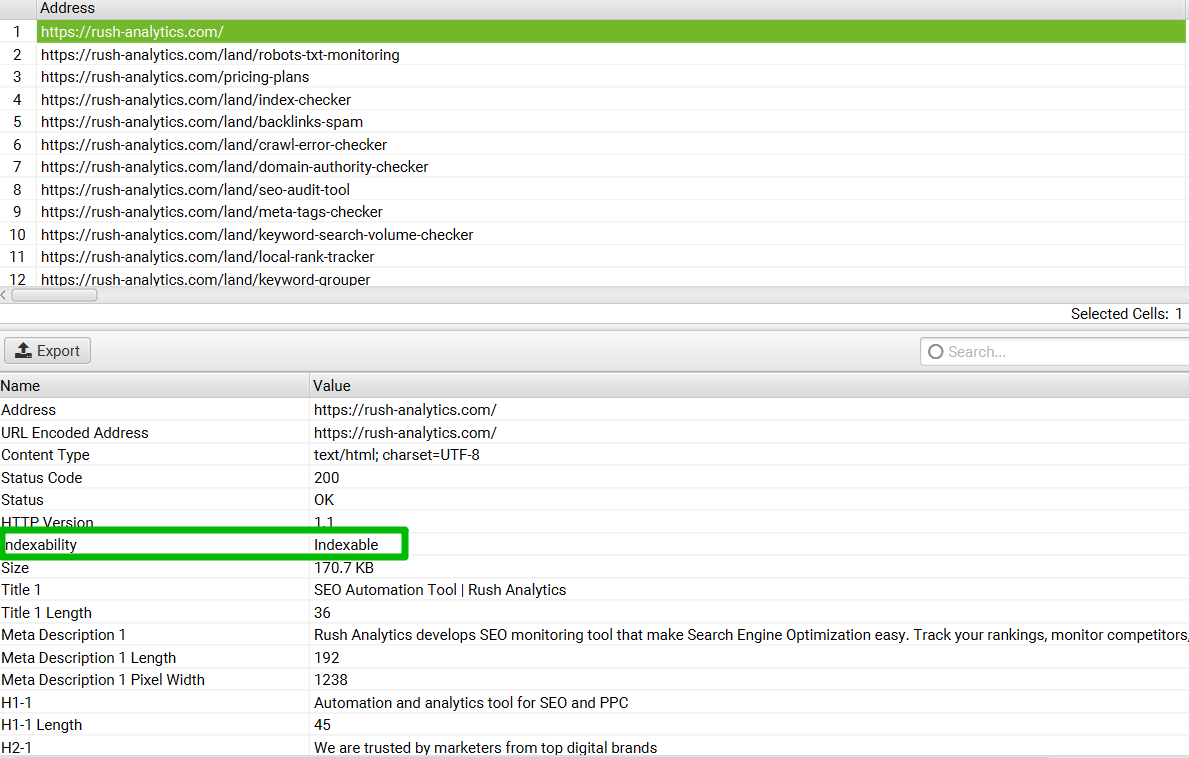
You can also check website’s crawlability and indexability with Screaming Frog SEO Spider. This tool is designed to crawl websites. It provides detailed info on many SEO aspects, including indexability. Download and install Screaming Frog SEO Spider on your computer to use it. Once installed, enter the URL of the website you want to analyze and start the crawl. After the crawl, go to the “Response Codes” tab. Filter the results to show only pages with a “200” status code. This means the page is crawlable but check the “Directives” tab to make sure it’s not blocked by robots.txt or meta robots tags. In the bottom panel you can see the indexing status in the “Indexability” line.
Method three: “site” command in Google
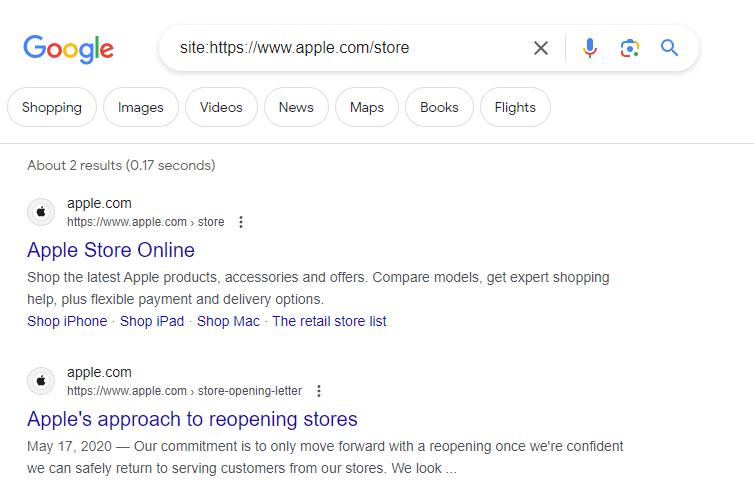
To check if a specific page is indexed by Google simply use the “site” command in the search engine. This command allows you to search for a specific URL or domain in Google’s index. To check if “https://www.example.com/page” is indexed type “site:https://www.example.com/page” into Google. If it shows up, Google has indexed it. If not, it might not be indexed or there could be crawling issues. Using the “site”
command is a fast way to check without extra tools.
Method four: check in bulk
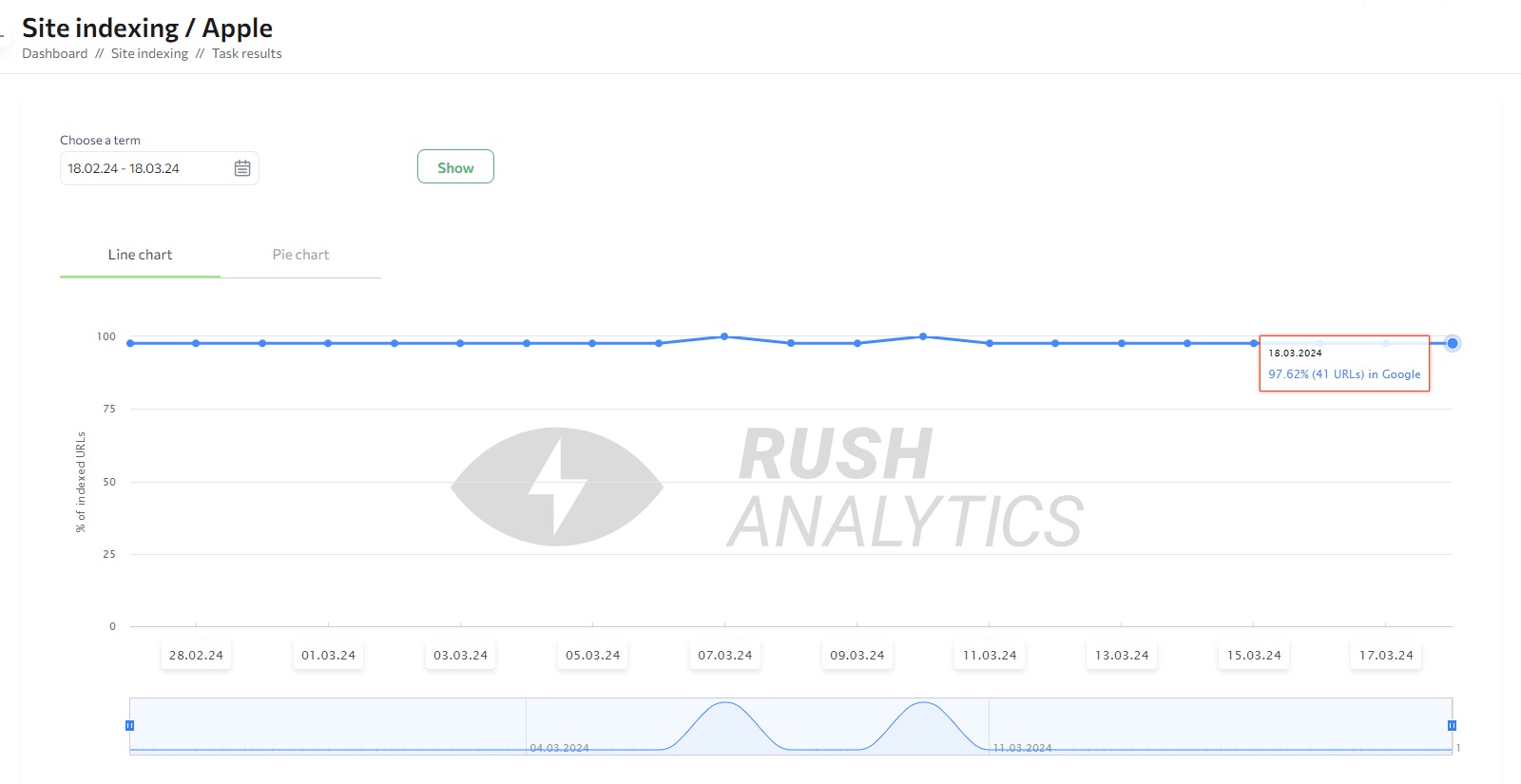
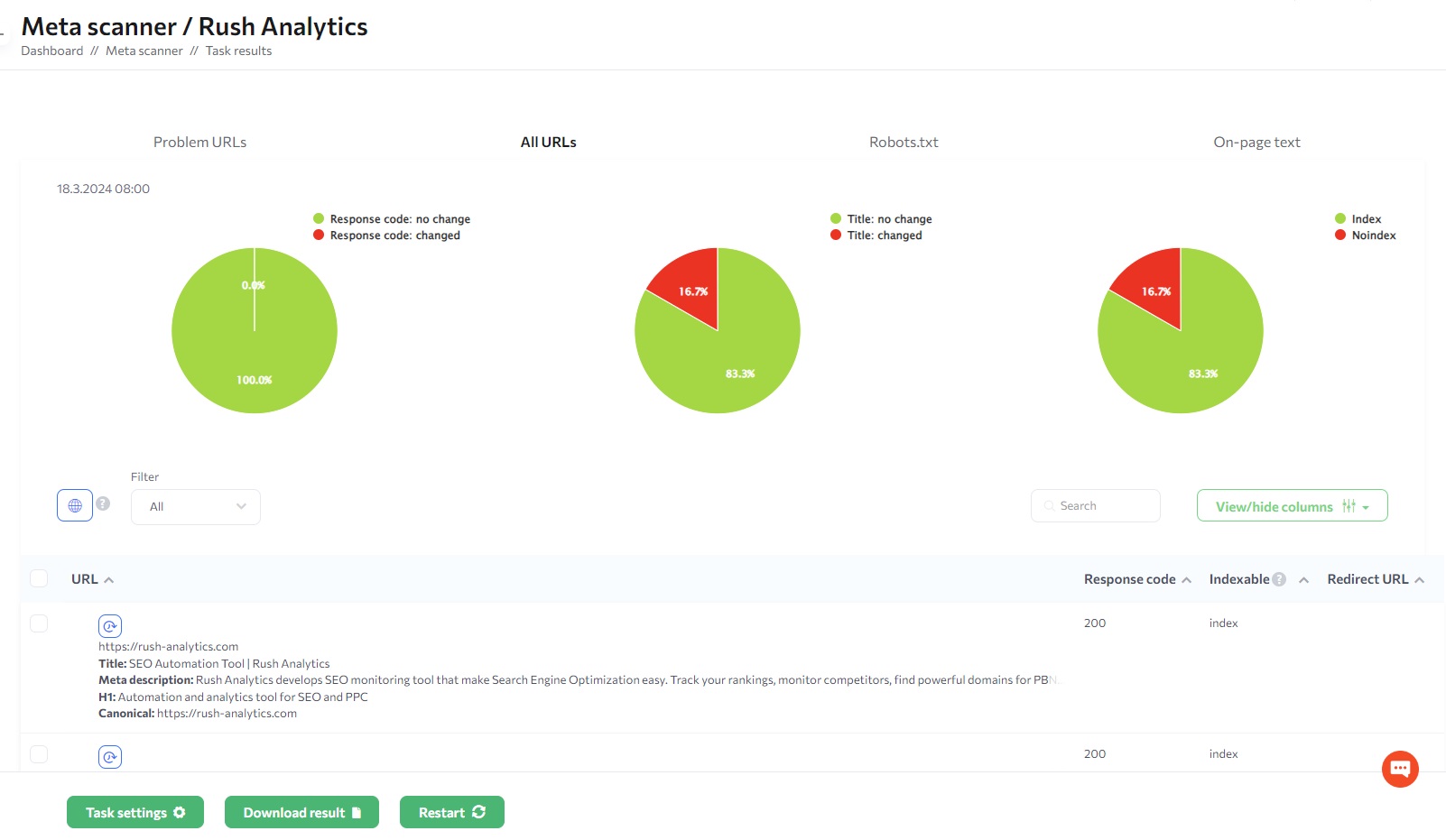
Rush Analytics has a set of tools to check your website’s indexation status and meta tags for many pages at once. The Google Index Checker lets you check up to 100,000 web pages in just 10 minutes. Just add your URLs as a list, Excel file, or sitemap.xml link. Pick Google and get a report on each page’s indexation status. This helps you find indexing problems, track new content, and improve your backlinks.
Also, The Meta Tag Checker tool is helpful for checking indexability. It allows you to verify if search engines can properly index your website’s pages. Additionally, the tool lets you track changes in your site’s title tags and H1 headings. It also lets you track changes in meta descriptions, robots.txt files, and response codes. You can set up daily monitoring with flexible settings and email alerts. This way, you can quickly spot any unexpected changes. They could affect your site’s traffic. Then, you can take prompt action to fix the issue and improve crawlability and indexability.
What affects crawlability?
Crawlability determines if search bots can find your site’s content. They need to access and index it for search. Let’s explore the key aspects that influence crawlability.
Internal Linking
Internal linking is key for SEO. It helps search engines find and understands your content. Use descriptive keywords in your links. Make sure all important pages are linked. Check for any unlinked pages. Good internal linking makes your site easier to crawl, spreads link value, and guides users to relevant content. This boosts your site’s performance and brings in more targeted traffic.
SEO-friendly site structure
A site’s structure must be SEO-friendly. Make sure that internal link structure is made in a way search bots can easily crawl and index your site’s content. Organize your content into clear, logical categories. Use a hierarchical structure, short URLs, and breadcrumb navigation. Be aware of orphaned landing pages. They have no internal links to them. This kind of pages can harm your SEO. To learn more about orphaned pages and how to find them, read our article: What Orphan Pages Are and How to Find Them. Review your site structure often. Improve it to help search engine crawlers and drive targeted, organic traffic.
Robots.txt
The robots.txt file instructs search engine bots on which pages to crawl. This text file, located in your website’s root directory, acts as a set of instructions for web robots, helping control your site crawlability. Use your robots.txt file to tell search engines which pages to crawl or ignore. Be cautious. Incorrect implementation can hurt your SEO. It can stop search engines from indexing your valuable content.
Noindex tag
The noindex tag is an HTML meta tag. It tells search engines not to index a specific page of your website. To apply the noindex tag, add the following code to the `<head>` section of the HTML document for the page you want to exclude from search engine indexing:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">Use the noindex tag carefully to avoid accidentally preventing search engines from indexing important pages on your site. The noindex tag tells search engines not to show a page in search results, but they can still visit the page.
Canonical tags
Canonical tags tell search engines which version of a page to show in search results when there are multiple similar pages. To implement a canonical tag, add the following code to the `<head>` section of the HTML document:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/preferred-page">Replace ""
Sitemap.xml
A sitemap.xml file is an XML document. It lists all the important pages on your website. This makes it easier for search engines to find and crawl your content. A sitemap helps search engines understand your site’s structure. Include important page URLs. You can also add optional tags for the last modification date, change frequency, and priority. Submit your sitemap to search engines through tools like Google Search Console. This makes sure they know your site’s content and can crawl it well.
Duplicate text or technical page duplicates on the site
Duplicate content refers to big blocks of content. They appear on many pages within a website or across different websites. Duplicates on technical pages can happen for many reasons. For example, due to URL parameters, session IDs, or printer-friendly versions. Having the same content can confuse search engines. It dilutes link equity and hurts your rankings. To stop duplicate content, use canonical tags to pick the preferred page. Also, use 301 redirects to combine duplicate pages. Use the noindex tag or robots.txt file to stop indexing duplicate content.
Server issues
Google only gets content it can process in the first six seconds. For example, if Google does not get content in the first six seconds, it will not be able to retrieve the information. Google will consider such a page as empty and will not index it. Use webpagetest.org to test your page load time for the country where most of your users are located. You can also test in several countries if you have a global product.
Also, make sure that the site does not have server errors when it is bypassed by the Google bot. You can also check this in Google Search Console or by examining log files with information about how Google bot crawled your site.
Optimizing your website for improved crawlability and indexing
To help search engines crawl and index your website:
1. Create a clear and logical site structure
- Organize your content into different stages, categories, and subcategories
- Use a hierarchical structure with a clear navigation menu
- Ensure that all important pages are linked internally
2. Optimize your robots.txt file
- Which pages or sections of your site should be crawled or ignored
- Regularly review your robots.txt file to avoid accidentally blocking important pages
3. Use sitemap.xml
- Create an XML sitemap that lists all the important pages on your website
- Submit your sitemap to search engines through tools like Google Search Console
4. Implement canonical tags
- Use canonical tags to specify the preferred version of a page when multiple versions exist
- Ensure that search engines index the most relevant version of your content
5. Minimize duplicate content
- Identify and resolve any duplicate content issues on your site
- Use 301 redirects to join duplicate pages
- Implement the noindex tag or robots.txt file to prevent the indexing of duplicate content
6. Improve page load speed
- Optimize your website’s performance to make sure fast loading times
- Compress images, minify CSS and JavaScript files, and leverage browser caching
7. Make sure mobile-friendliness
- Make creating content for your website responsive and mobile-friendly
- Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to identify and fix any mobile usability issues
To improve your site’s visibility in search results, follow this checklist. Also, regularly check if search engines can crawl and index your site. This will help you get more organic traffic and search queries.
How to check the crawlability regularly
The Google Index Checker is a powerful tool. It gives valuable insights into how Google’s search engine crawls and indexes your website or individual pages. To use the Google Index Checker, simply enter URLs you want to check. The tool will then analyze the URLs and provide you with a detailed report on their indexing status.
Use the Google Index Checker to find out what’s blocking your content from showing up in Google’s search results. This will help you optimize your website’s SEO and ensure your pages are indexed. Also you can check new and old content indexing. You can also check your backlink structure so your links are on indexed pages.
Meta Tags Checker makes sure your website is indexable and SEO friendly. It does this by monitoring key elements like robots’ directives (noindex, nofollow). This will keep your website visible and ranking in search results pages.
You’ll be notified via email as soon as they change so you’ll be aware of all the issues and process on your site.
Follow these best practices and check your website’s crawlability and indexability regularly and you’ll be optimizing your website for better visibility in search engines, more relevant organic traffic and better serving your audience.
Conclusion
Ensuring your website is crawlable and indexable is fundamental to achieving visibility in search engine results. Without proper crawlability, even the highest quality content remains invisible to potential visitors who rely on search engines to discover your website.
As we’ve explored throughout this article, several key factors influence crawlability, including your site’s internal linking structure, site architecture, robots.txt configuration, meta tags, canonical tags, sitemap implementation, content uniqueness, and server performance. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in how search engine bots access, interpret, and index your content.
Regular monitoring of your site’s crawlability and indexability is not a one-time task but an ongoing responsibility. Tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog SEO Spider, Google’s site command, and Rush Analytics’ specialized tools provide valuable insights into how search engines interact with your website, helping you identify and address potential issues before they significantly impact your search visibility.
By implementing the optimization strategies outlined in this article—creating a logical site structure, properly configuring technical SEO elements, minimizing duplicate content, improving page load speed, and ensuring mobile-friendliness—you create an environment where search engines can efficiently crawl and index your content, ultimately improving your website’s organic visibility and driving more targeted traffic to your pages.
Remember that search engine algorithms and best practices evolve continuously, making regular crawlability checks and adjustments an essential component of any successful SEO strategy. By maintaining optimal crawlability, you build a solid foundation for all your other SEO efforts to succeed and ensure your valuable content reaches its intended audience.
