Google Search allows you to exclude unwanted websites from search results or from the entire Google index, so that no one can find a particular page from your site. This fundamental search exclusion capability is essential for anyone working with search engine rankings and optimization. You can do this by blocking specific domains, labeling sites, or removing personal information from results.
⚡ The fastest way to exclude a website from Google search results is to use the “-site:” operator in your search. To exclude a domain, use “-site:example.com” in your search. Google will then remove all pages from that site in the results.
Google search operators like -site: are powerful tools that give you precise control over search engine functionality. Whether you’re an SEO professional analyzing competitors, a researcher filtering out irrelevant sources, or a regular user seeking more relevant results, mastering these operators is crucial for effective web searching.
Let’s explore all the methods to exclude sites from Google search, from basic manual techniques to advanced automation strategies.
How To Exclude A Site From Google Search
The site exclusion syntax is remarkably straightforward, but mastering its nuances can significantly improve your search efficiency. Here’s everything you need to know about using the “-site:” operator effectively.
Basic Syntax and Usage
The fundamental search query syntax for excluding websites follows this pattern:
search term -site:example.comFor instance, if you search for “SEO tips -site:example.com”, you’ll see SEO-related pages from all websites except “example.com”. The domain exclusion works instantly, filtering out all pages from the specified domain.
Advanced Techniques and Best Practices
Advanced search techniques can make your exclusions more precise:
- Multiple Domain Exclusion: You can exclude multiple websites in a single search:
SEO tools -site:example1.com -site:example2.com -site:example3.com- Subdomain Specificity: Target specific subdomains while allowing others:
marketing tips -site:blog.example.comThis excludes only the blog subdomain but shows results from other parts of example.com.
- Using Quotes for Precision: When excluding domains with similar names, use quotes:
content marketing -site:"example.com"- Combining with Other Operators: Enhance your search query refinement by combining -site: with other operators:
intitle:"SEO guide" -site:wikipedia.org filetype:pdf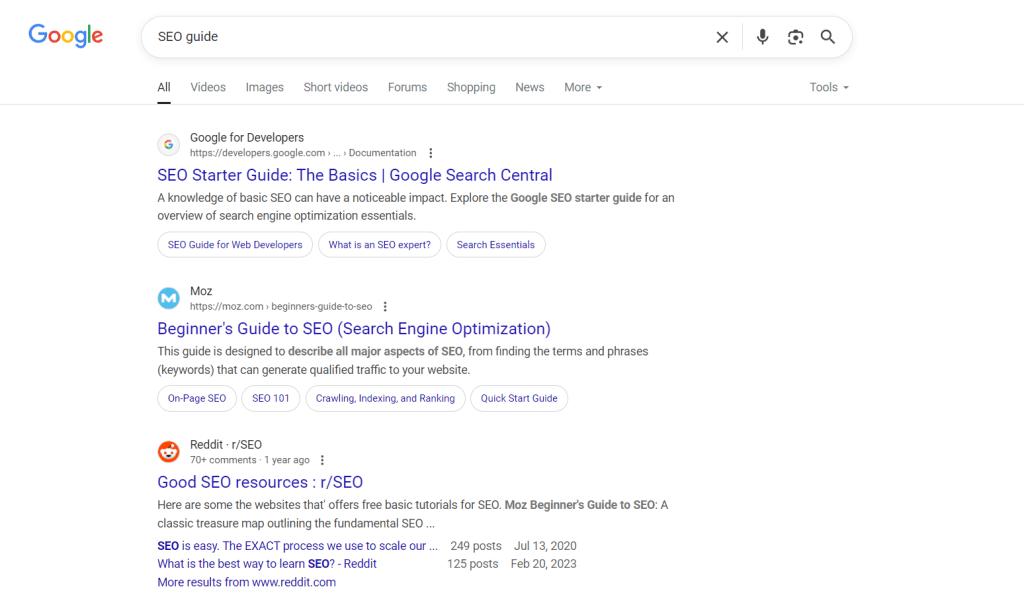
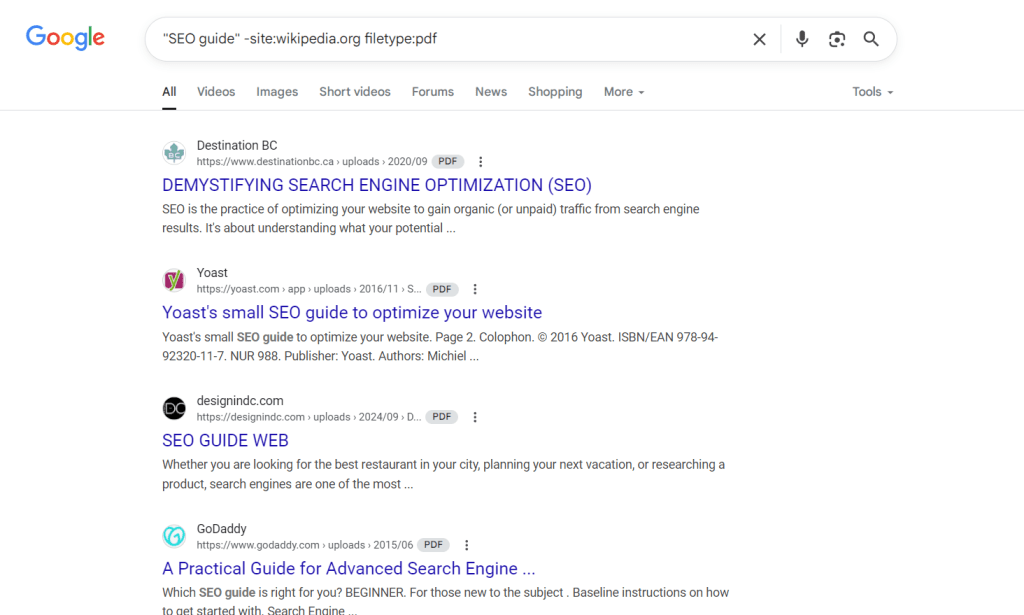
Important: Don’t add spaces after the minus sign. “SEO -site:example.com” works, but “SEO – site:example.com” doesn’t. This small detail is crucial for proper functionality.
These techniques help you exclude websites efficiently, whether you’re conducting competitive research, avoiding biased sources, or simply seeking fresh perspectives on familiar topics.
Automate Website Exclusion in Chrome Browser
If you frequently need to exclude certain websites from your searches, manually typing -site: operators becomes tedious. Fortunately, you can leverage search automation through Chrome search settings to permanently exclude unwanted domains.
Setting Up Custom Search Engine in Chrome
Here’s how to configure browser search customization for automatic website exclusion:
1. Access Chrome Settings
- Click the three dots in Chrome’s top-right corner
- Navigate to Settings → Search engine → Manage search engines
2. Modify Search Engine Settings
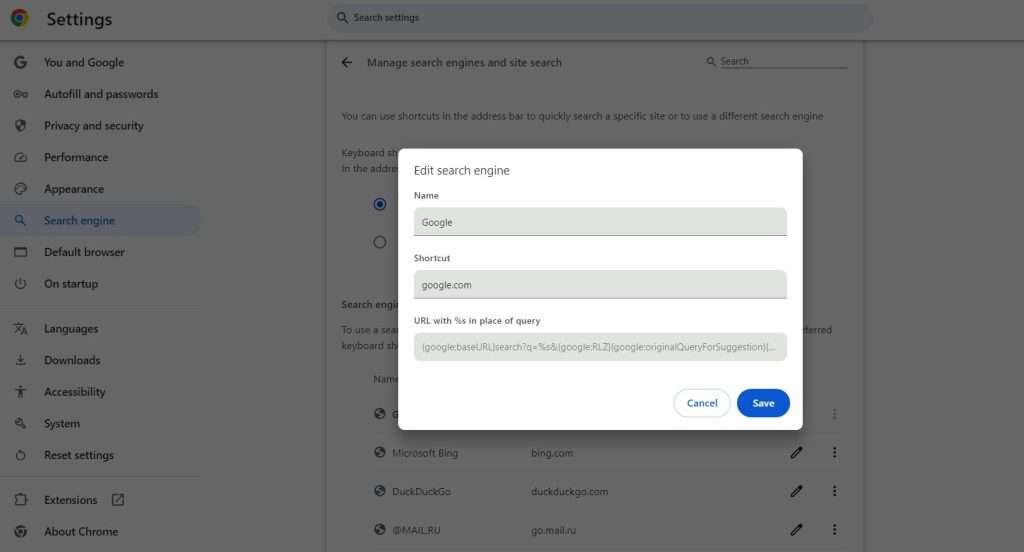
- Find Google in the search engines list
- Click the pencil icon to edit
- Copy the URL code from the “URL with %s in place of query” field
1. Create Custom Search Engine
- Click “Add” to create a new search engine
- Name it (e.g., “Google – No Reddit/Quora”)
- Set a keyword shortcut (e.g., “g”)
- Paste the copied URL code
2. Add Exclusion Parameters
In the URL field, add your exclusions after %s:
{google:baseURL}search?q=%s+-site:reddit.com+-site:quora.com&{google:RLZ}…
Excluding Top-Level Domains (TLDs)
The custom search engine approach is particularly powerful for excluding entire country-specific TLDs:
{google:baseURL}search?q=%s+-site:ru+-site:cn&{google:RLZ}…
This automatically filters out all .ru and .cn domains from your search results – perfect for travelers who want English results regardless of location.
Browser Settings Tips
When configuring browser settings for search automation:
- Set your custom search as the default to apply exclusions automatically
- Create multiple custom searches for different use cases (work, research, personal)
- Remember that these Chrome settings sync across devices when you’re logged into Chrome
Important: The URL structure may vary between users and Chrome versions. Always copy YOUR specific URL code rather than using examples from tutorials.
This automation method transforms how you interact with Google Search, making filtered results your default experience without any extra effort.
How to exclude your website from Google search?
To block websites or remove a webpage from Google search results, a simple solution is to add a specific HTML code called a meta tag to the page. This tag tells search engines not to index the content.
Using the Noindex Meta Tag
The noindex meta tag is the most reliable method for page indexation control:
- Open the webpage’s HTML code
- Locate the <head> section
Add the following meta robots tag:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">The “noindex” value instructs Googlebot and other search engines to exclude the page from their index. Once the tag is added to a specific page, save the changes and publish the updated page.
Implementation for Popular CMS Platforms
- WordPress: Use SEO plugins like Yoast or install headers/footers plugin to add the tag
- Shopify: Edit theme.liquid file in the <head> section
- Wix: Use the SEO settings panel for individual pages
Alternative Methods
X-Robots-Tag HTTP Header: For non-HTML files (PDFs, images), use server-side configuration:
X-Robots-Tag: noindexUnderstanding Robots.txt Limitations: While the robots.txt file can block crawling, it’s not recommended for preventing indexation. The rules in robots.txt govern crawling, not indexing. Pages can still appear in search results if other sites link to them, showing limited information.
Important: The noindex tag prevents indexing but allows crawling, while robots.txt prevents crawling but not necessarily indexing. For complete removal, use noindex.
Verification and Security
After implementation, verify your pages are deindexed using tools like Index checker. For sensitive content, consider additional password protection – this ensures content remains private across all search engines, not just Google.
Remember: Changes aren’t instant. Google must recrawl your pages to discover the noindex tag, which can take days or weeks depending on your site’s crawl frequency.
Why exclude certain search results in Google
As a website owner or digital marketer, understanding when and why to exclude sites from Google search enhances your search engine optimization efforts. Here are the most valuable use cases:
Refine Search Results
To obtain more precise search results with better search relevance, filter out websites that consistently provide irrelevant information. This search result filtering approach enables you to acquire information with accuracy.
For example, if searching for “yoga mats” but want to exclude marketplace results, use:
yoga mats -site:amazon.com -site:ebay.com -site:walmart.comThis reveals specialized yoga equipment stores and detailed reviews instead of generic product listings.
Monitor Featured Snippets
By omitting the current featured snippets holder, you can identify which domains might claim this valuable SERP features position next. This technique enables monitoring snippet changes over time.
For instance, if “wikipedia.org” holds the featured snippet for “Albert Einstein”, search:
Albert Einstein -site:wikipedia.orgThis reveals which sites Google considers next-best for the snippet, helping you understand the competitive landscape for these prime positions.
Analyze Search Engine Rankings
xclude top-ranking websites to better understand search engine rankings competition. This SEO analysis technique reveals which websites have potential to rank for your target keywords.
If analyzing “running shoes” rankings while excluding Nike:
running shoes -site:nike.comThis exposes second-tier competitors and upcoming brands, providing insights into ranking opportunities and content gaps you could fill to improve your own rankings.
Research Local Search Results
Filter out non-local websites to understand regional search landscapes better. When dealing with geoTLDs and location-specific results, TLD exclusion becomes crucial.
For “pizza delivery” in New York, excluding national chains:
pizza delivery New York -site:dominos.com -site:pizzahut.comThis surfaces local pizzerias and regional chains, giving clearer insight into local competition and opportunities for local SEO optimization.
Track Brand Mentions
Monitor brand mentions across the web by excluding your own domains. This helps track online reputation and discover unlinked brand references.
To find Microsoft mentions outside official channels:
Microsoft -site:microsoft.com -site:azure.com -site:xbox.comThis reveals third-party discussions, reviews, and news about your brand.
Monitor Search Result Fluctuations
Track search result fluctuations by excluding sites with stable rankings. This helps identify emerging competitors and algorithm changes.
For monitoring “travel destinations” volatility:
travel destinations -site:tripadvisor.com -site:lonelyplanet.comThis highlights newer sites gaining traction and helps predict future ranking shifts.
Advanced Search Techniques with -site: Operator
Mastering advanced combinations of search operators with -site: unlocks powerful research capabilities. These techniques go beyond basic exclusion to create highly targeted searches.
Combining Multiple Operators
The inurl: operator combined with -site: creates precise filters:
inurl:guide SEO -site:moz.com -site:ahrefs.comThis finds SEO guides while excluding major SEO platforms, revealing lesser-known but potentially valuable resources.
The site: operator can be used creatively with exclusions:
site:edu "machine learning" -site:stanford.edu -site:mit.eduThis searches educational institutions while excluding dominant universities.
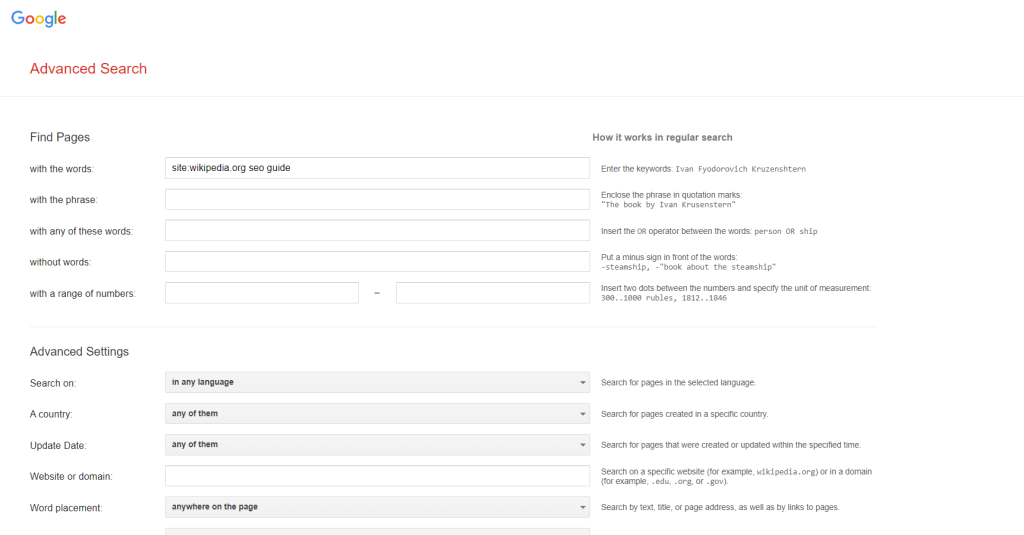
Google Advanced Search Page Integration
The Google advanced search page (google.com/advanced_search) provides a visual interface for complex queries. While it doesn’t directly support multiple -site: operators, you can:
- Use the interface to build your base query
- Add -site: operators manually in the search box
- Save the resulting URL for repeated use
Working with Search Limitations
Be aware of word limits in searches – Google typically processes around 32 words per query. When excluding many sites, you might hit this limit. Prioritize exclusions based on:
- Domain authority and prevalence in results
- Relevance to your specific research needs
- Geographic or language considerations
Practical Examples for SEO Research
Competitor Analysis:
"link building" guide filetype:pdf -site:competitor1.com -site:competitor2.comContent Gap Discovery:
intitle:"beginner's guide" cryptocurrency -site:coinbase.com -site:binance.comImportant: Some operators may not work perfectly together. Test combinations to ensure they produce expected results. The -site: operator is one of the most reliable and can be safely combined with most others.
These advanced techniques transform Google into a precision research tool, essential for SEO professionals and researchers requiring filtered, high-quality results.
How to Check if Your Site Is Still in Google Index
To check if your site is still in Google’s index, you can follow these steps:
1. Use the “site:” Operator in Google Search
Go to Google and enter the following command:
site:yourdomain.comReplace yourdomain.com with your actual domain name. This will show all the pages from your site that are currently indexed by Google. If no results are shown, it means your site might not be indexed.
2. Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides the most comprehensive indexation data:
- Sign in to Google Search Console
- If you haven’t already, verify your site in Search Console
- Once verified, go to the coverage report. This section shows which pages are indexed, excluded, or encountering errors
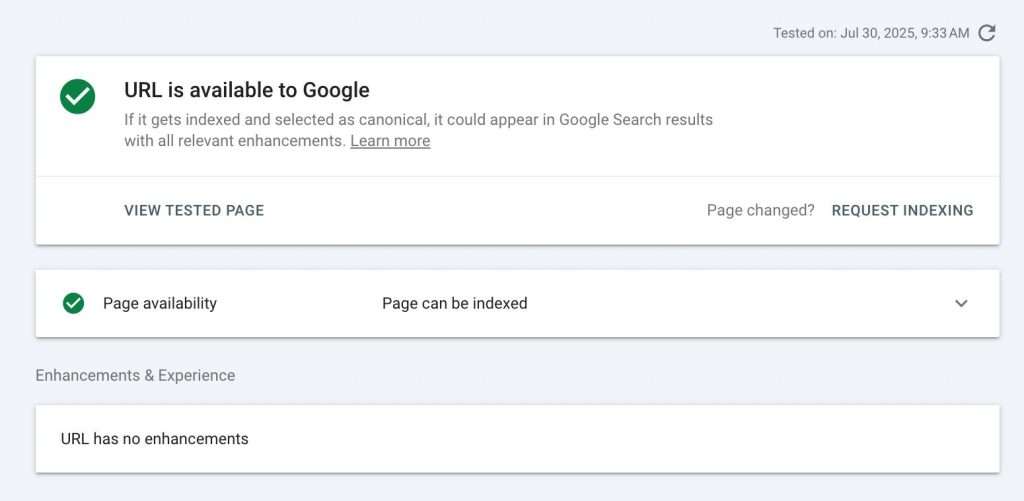
- Use the URL Inspection Tool to check if specific pages are indexed
The URL Inspection Tool provides detailed information about:
- Current Google index status
- Last crawl date
- Any indexing issues
- Mobile usability status
3. Use tools to check in bulk
If you need to check if your website or individual pages are indexed by Google, use the Google Index Checker tool. Professional index checker tools offer:
- Bulk URL checking capabilities
- Historical indexation tracking
- Automated monitoring and alerts
- Export functionality for reporting
Important: After making changes like adding noindex tags, you can submit recrawl requests through Search Console to speed up the process. However, Google will recrawl at its own pace based on your site’s authority and update frequency.
The Index checker tool specifically helps webmasters and SEO professionals identify indexed URLs, detect problems, monitor indexing progress, and improve SEO performance with the most competitive pricing on the market.
Final takeaway
Using the search engine techniques covered in this article, you gain complete control over the content of your Google search results. From basic -site: operators to advanced automation, these search result management tools empower you to find exactly what you need.
Whether you’re restricting access to certain sites, excluding irrelevant pages, or refining queries for more targeted information retrieval, these methods save time and increase productivity. The combination of manual techniques and automated solutions ensures you can adapt your approach to any search scenario.
Apply these tips and recommendations to manage your Google search experience effectively!
FAQ
Are there any tricks I can use when searching on Google?
Yes! Try extended search options to block sites or operators. Use a hyphen to exclude words, an asterisk as a wildcard, or quotation marks for exact matches. These help refine search results and find what you’re looking for quicker. Here is a comprehensive list of all Google search operators.
How do I stop a website from showing up in Google search?
Add <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”> to your webpage’s HTML <head> section. This instructs search engines to exclude the page from their index.
How do I remove a domain from Google search?
Use the “-site:” operator: –site:domain.com. For example, “smartphones -site:samsung.com” shows smartphone results without Samsung pages.
Can I automatically exclude sites without typing -site: every time?
Yes! Set up a custom search engine in Chrome settings that automatically appends -site: operators to all your searches.





