The aim of a copywriter is to create a catchy, informative SEO headline with relevant keywords to promote a web page in search engines. One type of headline is the title tag, which is displayed in search engines and affects the ranking and traffic to the page. Use our SEO tips to avoid common mistakes and create a catchy, effective titles that both users and search engines will like.
Title definition
Title is the title of a page, displayed as a link to the document in search results, in browser bookmarks, in posts on social networks. It is written in a larger font than the description, highlighted in blue (changing to purple when viewed) as a hyperlink and underlined when the computer mouse pointer is moved. Below the title, the description of the resource is often shown in the snippet.
A title tag is a meta tag that contains a short, precise description of the content of a web page and is considered a key tool in SEO website promotion. Title tag appears in the SERP and determines the clickability, traffic, and ranking (search engine position) of a page, which determine the success of a website. Search engine crawlers take the title into account when ranking a web page, checking its relevance to the page’s content and assessing its relevance to search queries.
The title tag of a web page is what makes users decide whether to click on a link. Therefore, it should be informative, interesting, attention-grabbing, and catchy. Copywriters are careful in creating website title tags, observing the optimal format, character limit and using standard templates.
Title in the HTML code of the page
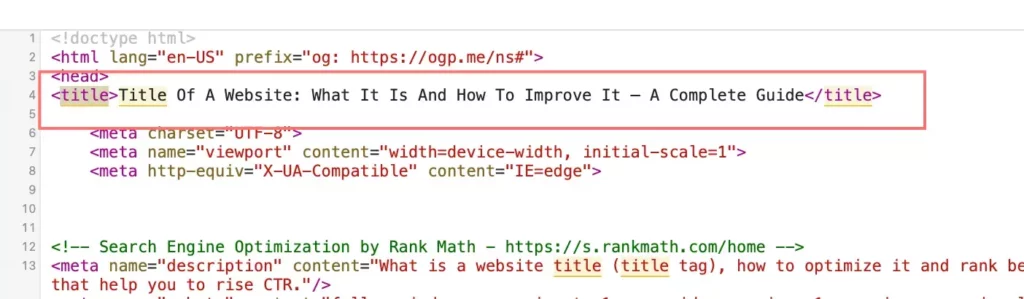
Title is an HTML element which is written in the <head> block of the HTML code of the website page. You can see it by pressing Ctrl + U at the same time, or by selecting “View Page Code” from the right-click context menu. The title tag is created separately for each page.
The user does not need to write the title tag in the HTML code of the page from scratch, because in most designers and content management systems (CMS), tags are added automatically. It’s enough to put the site on the WordPress engine and connect a multifunctional publishing plugin (Frontend Publishing Pro, Yoast Seo, WP User Frontend, etc.). The tag line sets the title of the document in search results, browser tabs (opens fully on mouseover), and social media posts.
In social media, the title appears as the title of a post when people share a link to a resource.
Making an optimized title tag
When compiling website titles, specialists take into account the peculiarities of search engines, type of content (informational or commercial), page content, and SEO-optimisation rules. Page title is based on the structure of the web resource and the formation of a keyword research, taking into account the frequency of queries. This process consists of the following steps:
- Keyword research. SEO experts make a list of search queries, analyse keywords and categorize words from queries into groups of unique words. They also take into account words from the highlighting in the results, thematic words (often found in the snippets of competitors) and keyword suggestions.
- Keyword clustering – distribution of keywords by pages (URLs). For the convenience of our specialists, we upload the tags to Excel.
- Formation of a title with the inclusion of relevant keywords to increase the relevance of the page content to user queries in search engines – Google, Bing, etc.
Pages with properly composed, optimized website title tags have high ranking in SERP – search engine results page. But the optimization process requires certain knowledge and skills, and therefore for effective page promotion it is carried out by experienced SEO-specialists.
Differences between title and H1 heading
Title and H1 are two types of header and different tags in HTML code markup with different functions. They may be the same, but preferably different. Title is the title of the web page in the search engine and on the browser tab, while H1 is the shorter title of the article displayed on the website page itself. Title tag is “SERP Tracker Tool — Rush Analytics”, H1 is “SERP keywords tracker tool”.
Title overlaps with H1 in terms of keywords research, because both contain the main keys to establish the relevance of the source to queries by search engines’ crawlers. Website title tags without keyword phrases can be determined by irrelevant user queries. A good website title is intended to convey the essence of the information contained in the source, attracting attention, engaging users, and serves as a tool to promote the web page. It should be interesting, intriguing, engaging, for example:
- “How to lose 10 kg weight in a month”
- “Ways to make fast money for the lazy”
- “The most common relationship mistakes”, etc.
Rules for a successful website title
When preparing to write a website title, experts take a look at the metadata of the top 10 pages in the SERP, analyze the list of keywords and think through how to fit them naturally. A page with a well-written title has a good chance of appearing in the Google search engine’s featured snippet.
A snippet is a small portion of text, expanded upon the description, containing keywords for a search query from a page on the site. It is located on the first line of search results, above the competing pages, which significantly increases the clickability of the resource.

Basic rules for making a good website title
- Follow the language rules. Title tags should reflect the content of the document, be readable and easy for users to understand. Grammatical rules should be followed, consistency, inflection of words should be ensured. Numbers have a positive impact on clickability (“Top 10”, “Top 5”). The grammatical number should be chosen on the basis of the contents of the material: for a product card – singular; for a listing – plural. Keywords should be typed naturally and evenly spaced. The keyword “mask tailoring” is unreadable in the exact entry; it can be typed “Masks tailoring: popular models and colors”.
- Check if the size is optimal. Title size is 69 characters (12-13 words) in Google, but the average optimum length is 44-60 characters. Avoid too short headlines of 2-3 words, as it lowers their relevance. Long headlines exceeding the character limit are also indexed, but they are truncated or hidden behind the ellipsis in the search results. In this case, the robot takes into account when ranking the entire title, not just the visible part of it.
- It is advisable to form the title into a single sentence. Website title tags consisting of two sentences usually rank low, appearing on page 3-4 of Google. The tag “Handmade postcard in half an hour. How to decorate a card beautifully” isn’t appropriate: it has 2 sentences and incorrect inflection. The correct version is “How to make a beautiful handmade card in half an hour”.
- The presence of the main keyword in the direct occurrence. The main keyword or phrase does not need to be declined, diluted, if they can be fit harmoniously into the title. The key phrase “the dog has lost his appetite” can be written “Why has the dog lost his appetite?” The most frequent and competitive keyword is usually inserted at the beginning of the title, as the first word or phrase has more weight in the ranking than others. Also, they will not disappear from the visible part of the title if they are shortened. To improve ranking, keywords are diluted with low-frequency (LF), medium-frequency (MF) queries. Key phrases like “plastic windows delivery” are inflected and diluted for readability.
- Avoid keyword stuffing and spam. Use title naturally and don’t repeat the same keyword in different forms: search engines perceive this as spam, which can lower the site ranking. Instead of headline “British Cat: photo, character, education, care, nicknames” the right solution will be “All about the British breed of cat”, or you can write articles for each query with separate titles: “Character, behavior…”, “Education and training…”, “What to feed…”, “30 popular nicknames…”, etc. With such a breakdown of texts and internal linking between the articles on the site it is possible to increase traffic, the level of trust of the search engine to the website (trust) and the specific weight of each URL.
- No exaggerations. The title tag is the title of one page, not a description of the whole site. It should accurately match the content of the material, without exaggeration or obfuscation. You don’t need to add extra words to it that are irrelevant to the article or are missing from the search terms. Irrelevant tags may be subject to search engine sanctions (discounting). A user, who liked the content of the site or product design in the online shop, will independently visit the other sections of the resource. No need to insist on it intrusively. Also, no need to specify in the title of what is not on the page. If there is a task to write about the causes of arthritis, do not need to mention in the title of the treatment of this disease. The user will not get this information and the credibility of the site will be lost.
- Keep punctuation to a minimum. These punctuation marks should not be used . , !, +, -, =, ‘. Allowed: , -, ?, , rarely – ” “. A long dash (–) is used to separate several queries; semantic blocks are separated by a vertical | stick. The Title in question form must end with an appropriate sign. Search engines support special characters &, ©, ®, ™, -, §, £, €, °, “, ¼. It is worth avoiding unnecessary characters, and if they are added, to analyze the clickability rate (CTR). A maximum of one emoji may be inserted into the title, separated from the words with spaces.
- Use a brand name, if it’s popular. Name of well-known brands, firms, websites inserted at the beginning, after the main key or at the end of the title to make it memorable and increase conversion rate (CR): “All SEO Tools In One Platform | Rush Analytics”, “Website promotion – Wikipedia”. World-renowned brands place the title at the beginning as a familiar name for many users, evoking trust. This practice also improves brand visibility and attract clicks.
- Respect for uniqueness, don’t duplicate web page titles. Website title tag should be original, not identical to other pages of the site. It should not repeat words to avoid overspam. Instead of “Notebook Asus – buy Asus laptop with delivery in New York” correctly write “Buy Asus laptop with delivery in New York”.
- Minimize stop words. Stop-words (conjunctions, prepositions, particles, pronouns, introductory structures) make a headline unique and readable. But a good practice is to minimize their number. Search engines do not take stop-words into account when evaluating a headline, but their presence may also affect ranking. On the query “sale and rent of bicycles in New York” the site is at 3 place in the search results, while when you enter the query “sale and rent of bicycles New York” the same page takes 2nd place in the list of pages.
- Make websie titles of commercial pages in the same style. Titles for the same type of pages of goods / services are made in a template consisting of the name of the product / service, call to action the words “buy”, “rent”, “order”, “price”, indicating the region, brand name, shop. Example: “Quality bed linen – buy cheap in New York”. It’s not recommended to use adjectives such as “profitable”, “best”, “large” in selling text. Specifics and information on special conditions (discounts, promotions) have a good effect on clickability.

Analyzing the effectiveness of a title
When evaluating the effectiveness of communication channels, all components of SEO-promotion are monitored holistically, so it is not possible to analyze the success of a single title. In this case, A/B testing is used to determine the effectiveness of individual, competitive titles after 2-3 weeks of measurement.
The main indicators taken into account when evaluating the effectiveness of a website’s tagline is CTR.
Clickability (CTR) – the ratio of the number of clicks to the number of impressions, expressed as a percentage. The higher the indicator, the more often users click to the page. CTR can be analyzed via Google Search Console: “Search results”, “+New”, “Page”.
Editing the title after indexation
If the page is at the top and has a lot of traffic from search engines, you do not need to change the title. But if the title has been indexed by a search engine and has not “shot”, that is, stably (1-5 months) is held at low positions in extradition, it should be edited (no more than 1 time in 3-4 weeks). SEO specialists, based on statistical research on traffic, user behavior and analysis of the top results, optimize the title by adding new words, changing the word forms etc. for higher ranking. When changing the title, it is also worth changing the H1 and the page content related to it.
Conclusion
A ‘title’ is a link to a page in a search engine listing that will take users to a website. It is a key tool for website promotion, influencing clickability, traffic and page ranking, on which depends the further success of the resource. With knowledge of search engine algorithms, SEO-promotion trends, peculiarities of title tag and following simple rules of its composition, you can improve page ranking, get more clicks and drive traffic to your website.






