The internet offers amazing benefits but also contains potential dangers. Various authorities have implemented protective measures like URL blacklisting to make the web safer.
URL blacklist is a collection of websites flagged as dangerous by search engines. When a site appears on this list, users see warning messages instead of the website.
Google’s Safe Browsing system flags thousands of websites daily. For site owners, blacklisting means traffic drops, reputation damage, and loss of access to services like Google Ads.
If your site gets blacklisted, fixing it should be your priority. Blacklisting isn’t permanent if you take appropriate action. Understanding causes, prevention, and solutions is essential for website owners.
What Is URL Blacklist?
A URL blacklist is a database of websites flagged for suspicious or malicious activity by authoritative bodies. These include search engines, antivirus providers, and security services that monitor web safety.
When users visit a blacklisted site using Chrome or another major browser, they see a warning screen instead of the website. This screen appears with red background and clear warnings. The message varies based on the threat:
“The site ahead contains malware” indicates harmful code.
“Deceptive site ahead” suggests phishing attempts.
“This site may harm your computer” warns about potential risks.
Blacklisting severely impacts search visibility and traffic. Search engines remove blacklisted sites from their results entirely. Even people searching for your brand might not find you.
Google sometimes alerts website owners through Search Console. The notification specifies the issue and applies penalties until problems are fixed.
While users can bypass these warnings, most choose to leave. Studies show over 95% of users exit immediately upon seeing security warnings. Even temporary blacklisting can devastate your website traffic.
Google Blacklist
Google maintains extensive lists of dangerous websites through its Safe Browsing system. This system uses algorithms and user feedback to identify harmful sites. Google officially uses “blocklisting” rather than “blacklisting,” though many still use both terms.
Google categorizes harmful websites into three types:
- Social engineering (phishing) pages: Sites that trick users into revealing sensitive information.
- Malware pages: Sites containing code that downloads and installs software without consent.
- Unwanted software pages: Sites promoting software that violates Google’s Software Principles.
Google’s blocklisting has grown significantly. In 2026, they blacklisted about 10,000 websites daily. Today, they flag nearly 40,000 websites weekly.
While blocklisting protects users, it creates challenges for compromised legitimate sites. Blacklisted sites experience:
- Removal from search results.
- Warning screens in browsers.
- Sharp traffic decline.
- Loss of consumer trust.
- Reduced revenue.
For businesses relying on organic traffic, blacklisting can cause substantial financial losses. Even after fixing issues, restoring previous traffic levels takes time.
Why Would a Site Be Blacklisted?
Understanding blacklisting causes matters for both users and site owners. Users learn about risks, while owners gain insight into prevention and faster resolution.
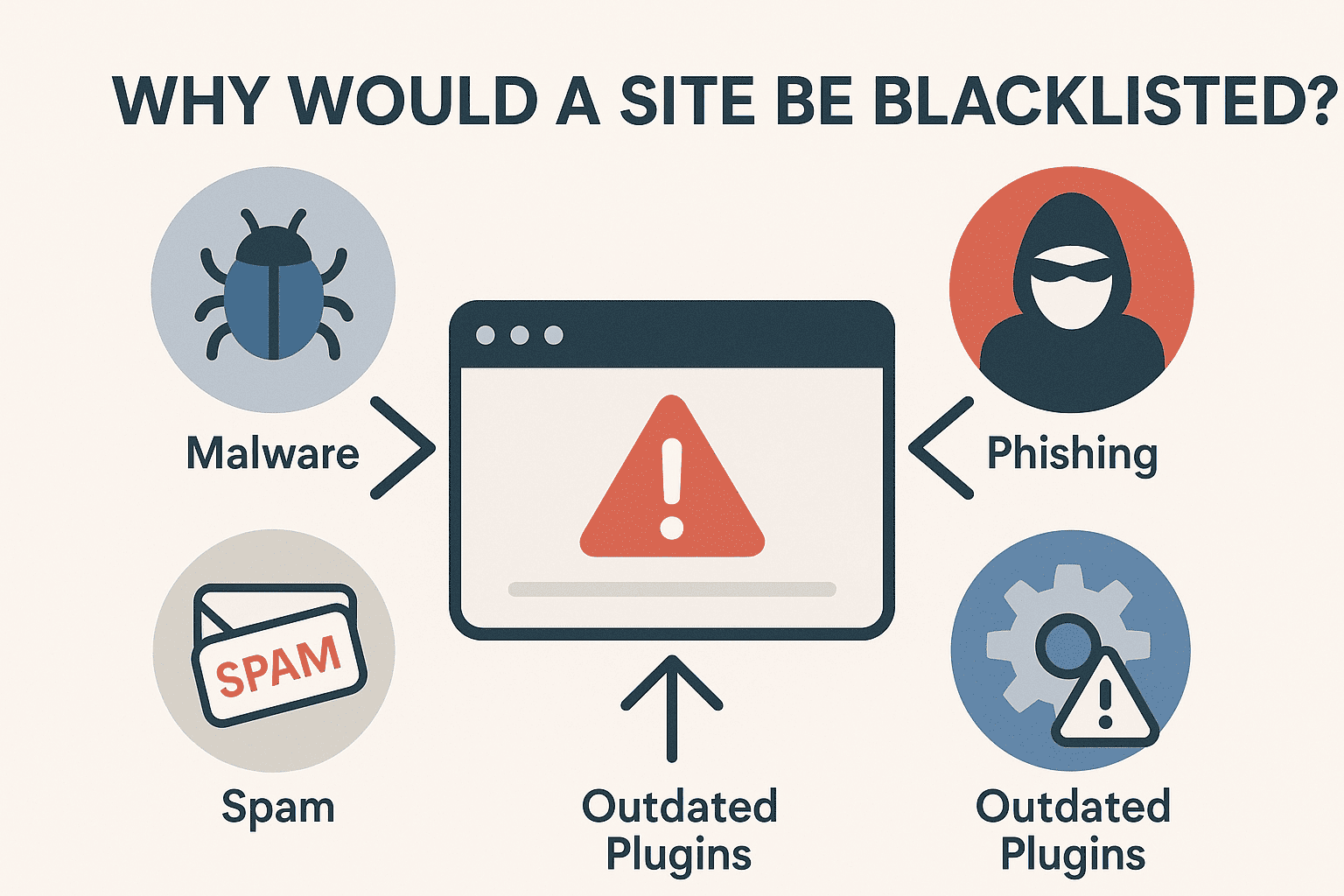
According to Google, most blacklisting happens for three main categories of problems.
Malware
Malware refers to software designed to harm device security or user safety. Trojans disguise as legitimate programs to trick users into installation.
Various malware types trigger blacklisting:
- Viruses: Programs that replicate through other programs
- Adware: Unwanted advertisements linking to harmful sites
- Spyware: Programs secretly collecting user information
- Ransomware: Software locking files until payment
- Botnets: Networks of infected computers for attacks
Even legitimate sites can get blacklisted due to false positives when outdated plugins contain code resembling malware.
Unwanted Software / Using Unsafe Plugins
Google classifies software as “unwanted” when it uses deception, changes settings unexpectedly, or collects personal information without disclosure.
Websites often get blacklisted from unsafe plugins. Using unverified sources creates security risks. Outdated plugins represent another major risk as developers regularly patch security vulnerabilities.
Always verify developer credibility before installing any plugin. Malicious developers embed harmful code within seemingly helpful tools.
Social Engineering / Phishing Schemes
Social engineering tricks users into dangerous behaviors. Phishing is the most common form, with sites getting blacklisted when flagged for such activities.
Phishing occurs through embedded links or entire fake websites impersonating legitimate services. They aim to collect passwords, financial details, and personal information.
Attackers often embed phishing links on hacked websites without owner knowledge.
SEO Spam
SEO spam was found in 62% of infected websites cleaned by Sucuri in 2026. It ranges from keyword stuffing to sophisticated hacking.
Hackers compromise well-ranked websites to inject spam onto high-performing pages, promoting counterfeit products or scams. They target established sites rather than trying to rank their own scam sites.
These injections often hide in areas rarely checked, making SEO spam particularly effective as a black hat technique.
How to Avoid Being Blacklisted
Preventing your site from getting blacklisted requires proactive security measures. These strategies help keep your website off blacklists and protect your brand’s credibility with both search engines and users.
Quality hosting providers offer essential security features. These include continuous monitoring, strong firewalls, and built-in protections. Such features help detect vulnerabilities and prevent attacks before they compromise your site.
Good hosting providers also alert you to suspicious activity and assist with recovery if infection occurs. While a comprehensive list of all security measures would be extensive, let’s focus on the most effective strategies for blacklist prevention.
Use a Credible Hosting Provider and Automated Cybersecurity Service
Choosing a reputable hosting provider with robust security measures forms the foundation of website protection. Your site’s reputation partly depends on your hosting environment. Association with a host that has many blacklisted sites can negatively impact your own site’s reputation.
Look for hosting providers offering:
- Regular security updates
- Malware scanning
- Intrusion detection
- DDoS protection
- Secure server configurations
Beyond hosting, consider dedicated security solutions like Sucuri, SiteLock, or Wordfence. These services provide comprehensive protection including:
- Regular malware scanning
- Threat removal
- Web application firewalls
- Security monitoring
- Blacklist monitoring
Regular scanning enables prompt detection and resolution of malicious activity. This proves especially important for website owners whose hosting providers don’t offer adequate monitoring services.
Keep Your Software and Third-party Apps Up-to-date
Maintaining updated software, plugins, and apps strengthens your website security dramatically. Outdated components create vulnerabilities hackers can exploit to infiltrate your site.
Once inside, attackers might install malware or allow spammers to inject unwanted content. Updates often contain security improvements or bug fixes addressing known vulnerabilities.
Failing to update creates backdoors or insecure entry points that compromise your website. Many successful attacks exploit known vulnerabilities that patches have already addressed. Keeping systems updated closes these security gaps.
If you find outdated plugins lacking developer updates, remove or disable them. Continuing to use abandoned plugins significantly increases your security risks and chances of blacklisting.
Only Use Trusted Software
Free software tempts many website owners, but caution is essential. Without proper vetting, free software may contain malware or create security vulnerabilities that lead to blacklisting.
Verify software credibility through these checks:
- Download numbers: Popular downloads with many users typically undergo more scrutiny
- Reviews: Read what other users say about security and reliability
- Developer research: Investigate the company or individual behind the software
- WordPress compatibility: Ensure compatibility with your current WordPress version
- Update frequency: Check when the software was last updated
For WordPress plugins, look at the last update date in the WordPress repository. Plugins without updates in the past six months might indicate abandonment by developers. This increases the risk of unpatched security vulnerabilities.
Thoroughly investigate before installing any third-party software. The momentary convenience of free software isn’t worth the potential blacklisting and business disruption that might follow security breaches.
Require Strong Passwords and Limit Login Attempts
Hackers commonly use dictionary attacks to gain unauthorized website access. These attacks involve guessing passwords from lists of commonly used words. Alternatively, brute-force attacks use automated bots to rapidly test billions of potential username-password combinations.
Both attack methods target weak passwords and unlimited login attempts. Requiring strong passwords with varied character types provides effective defense against such attacks:
- Uppercase and lowercase letters
- Numbers
- Special symbols
- Minimum length requirements
Limiting login attempts prevents brute-force success by blocking access after several failed attempts. These practices are particularly important for membership sites or websites with multiple backend users.
Consider passwords longer than 12 characters for maximum security. Password generators help create complex, unique passwords. Password managers like LastPass or 1Password help users store and organize these strong credentials securely.
Rush Analytics security monitoring can identify unusual login patterns that might indicate attempted breaches. Setting up alerts for multiple failed login attempts helps catch potential attacks early.
Prevent User-generated Spam
Websites allowing user contributions face unique security challenges. Comments, reviews, and forum posts provide opportunities for malicious actors to insert harmful links or content.
Implement these protective measures:
- Publish clear abuse policies defining acceptable content
- Create user reputation systems that initially tag new users’ content with “noindex”
- Develop blocklists for repeat offenders
- Use reCAPTCHA to prevent automated spam account creation
- Moderate all user-generated content before publication
Google Web Risk API offers another valuable tool. This service checks website URLs against Google’s database of unsafe sites. When a user submits content containing links, the API can verify those links against known threats.
This tool proves particularly useful for websites with significant user-generated content. The risk of unsafe links increases proportionally with user contribution volume. Implementing automated checking reduces the likelihood of inadvertently hosting harmful links.
Rush Analytics link monitoring tools can help identify suspicious patterns in user-submitted content. Regular scans detect potentially harmful links before they trigger blacklisting actions by search engines.
Assign User Roles and Permissions
When multiple people access your website, assigning appropriate user roles and permissions becomes crucial for security. This practice limits potential damage if a hacker compromises one user account.
With administrator credentials, hackers can cause extensive harm – installing malware, creating backdoors, or adding malicious content. However, compromising an account with restricted permissions limits what attackers can accomplish.
Implement a least-privilege approach, giving users only the permissions necessary for their specific tasks. For example, content creators might need publishing rights but not plugin installation capabilities. This minimizes security risks while maintaining workflow efficiency.
Regularly audit user accounts and remove unnecessary access rights. Deactivate accounts for individuals no longer working with your website. Each active account represents a potential entry point for attackers, so maintain only those absolutely necessary.
Replace Broken Links
Broken links create unexpected security vulnerabilities when they point to domains that malicious actors have repurchased. Links typically break when referenced sites restructure without proper redirects, resulting in 404 errors.
While these errors harm user experience and SEO rankings, the security implications prove even more concerning. If linked domains change ownership, these links could redirect to malware or phishing sites, potentially causing blacklisting.
Conduct regular site audits for broken links using tools like:
- Google Search Console
- Rush Analytics SEO audit tools
- Screaming Frog
- Broken Link Checker plugin for WordPress
When identifying broken links, don’t simply remove them. Evaluate their purpose in your content and replace them with current, relevant alternatives. This maintains content value while eliminating security risks.
Automated tools simplify this process by scanning your entire site and reporting all broken links. Some tools even suggest replacement links based on content context, streamlining the correction process.
Monitor Website’s Health
Regular website health monitoring helps detect security issues early, before they trigger blacklisting. Implement these monitoring practices:
- Use Google Analytics to track traffic patterns and identify suspicious drops
- Check Google’s Security Issues report page to identify potential hacked pages
- Set up Search Console alerts for malware detection
- Use Google Web Risk API to check URLs against Google’s database
- Try online tools like Sitechecker’s blacklist checker for regular status updates
To access Security Issues in Google Search Console, verify site ownership first. Once verified, navigate to the Security Issues tab to see if Google has flagged any problems potentially leading to blacklisting.
Rush Analytics offers comprehensive website monitoring tools that can alert you to potential security issues before they result in blacklisting. Regular scanning identifies vulnerabilities, malware, and suspicious activity patterns early enough for preventative action.
Your URL Is Blacklisted: What Now?
Despite best preventative efforts, blacklisting sometimes occurs. If your website gets blacklisted, understanding the recovery process helps restore your online presence quickly and effectively.
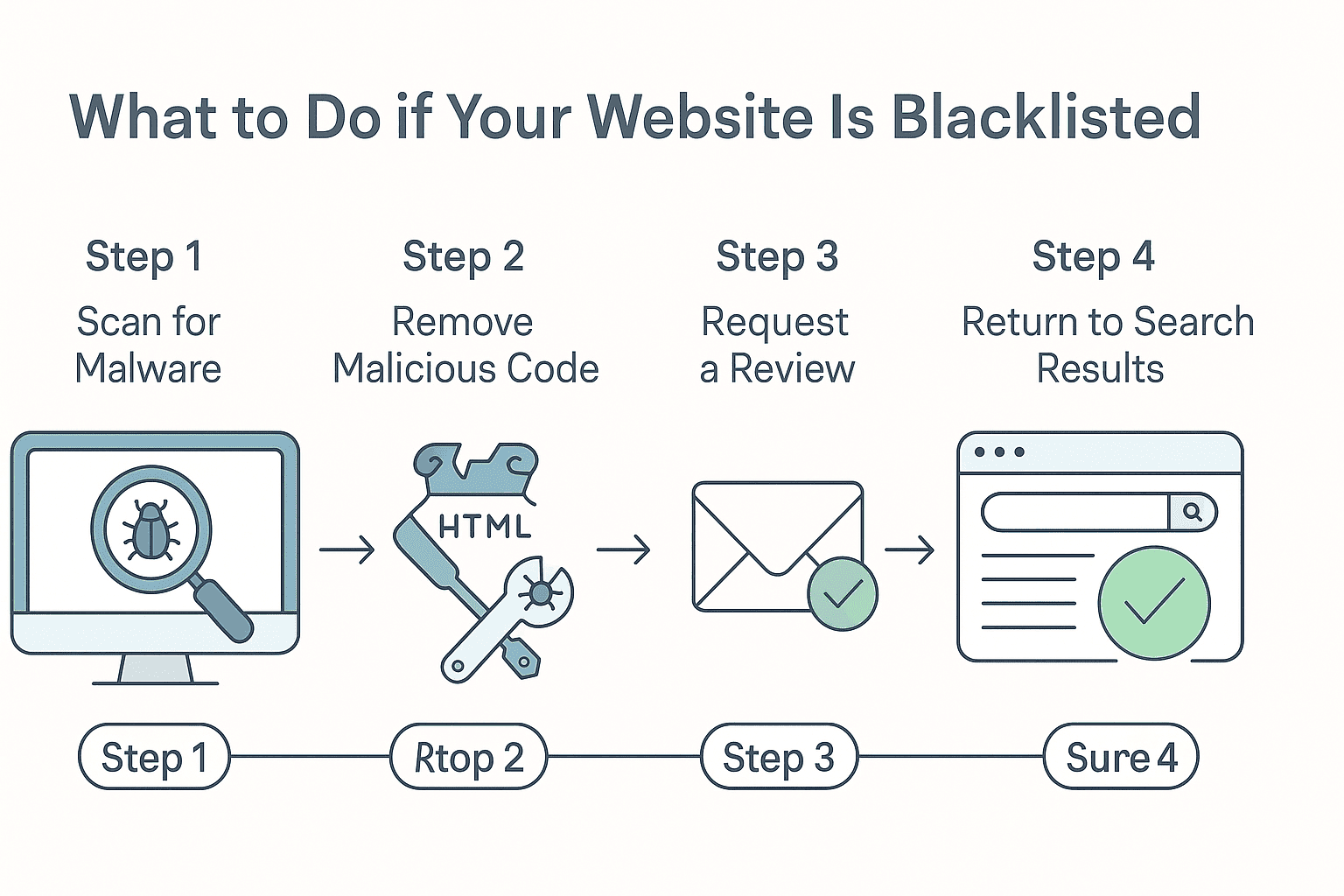
The general process involves thoroughly cleaning your site of problematic code and harmful content. After addressing all security issues, you must request a review to have your domain removed from blacklists.
While the specific steps vary slightly between different blacklisting authorities, the fundamental approach remains consistent. Let’s examine the recovery process in detail to help you navigate this challenging situation efficiently.
Step 1. Remove the Infection or Content From Your Website
The first critical step in blacklist removal involves identifying and addressing the underlying security issues. You have two options: handling it yourself or hiring professional assistance.
For the DIY approach:
- Back up your website before making changes. Use plugins like UpdraftPlus for WordPress sites.
- Scan for malware using security tools to locate infected files.
- Clean WordPress core files by comparing them with official versions from WordPress.org.
- Check wp-config.php for unfamiliar code that might indicate compromise.
- Reinstall WordPress core files from official sources.
- Update all plugins, themes, and integrations to their latest versions.
- Apply security patches recommended by your hosting provider.
- Strengthen account security with new, strong passwords and two-factor authentication.
This process requires technical knowledge and careful attention to detail. Missing even small malicious code fragments can result in continued blacklisting.
Alternatively, professional cleaning services offer expertise and comprehensive solutions. Providers like Sucuri, MalCare, Wordfence, and SiteLock specialize in removing malware and resolving security issues. While these services typically start around $100-$200 per cleanup, they offer guarantees and ongoing protection.
Rush Analytics security services can help identify the specific issues causing your blacklisting. Our detailed reports pinpoint problem areas, making remediation faster and more effective than manual searching.
Step 2. Submit Your Website for Review
After securing your website, request a review to have it removed from blacklists. For Google blacklisting, the process works through Search Console:
- Access your Google Search Console account
- Navigate to the Security Issues tab
- Click “I have fixed these issues” button
- Select “Request a review”
- Provide detailed information about the steps taken to resolve the problems
Be thorough when describing your remediation efforts. Include specific actions taken, files cleaned, security measures implemented, and ongoing prevention strategies.
Google’s review process typically takes several days. If they determine your site is now secure, they’ll remove it from their blacklist and restore normal visibility in search results.
For non-Google blacklists, contact the security firm or ISP directly. Each maintains different review processes, but most require similar information about the steps taken to secure your site.
Patience is essential during this phase. Rushing or submitting incomplete information may result in failed reviews, prolonging the blacklisting period. Provide comprehensive details and allow adequate time for thorough evaluation.
Prevent Future URL Blacklisting
Once your site returns to good standing, implement ongoing security measures to prevent future blacklisting:
- Install reliable security plugins or firewalls that actively monitor for threats
- Schedule routine security scans and virus checks, at least weekly
- Limit user permissions to reduce potential damage from compromised accounts
- Regularly monitor website traffic and content for anomalies that might indicate breaches
Moving beyond basic understanding of blacklists to implementing continuous protection provides the best defense against future incidents. Proactive security management prevents the traffic loss, reputation damage, and recovery costs associated with blacklisting.
Rush Analytics offers ongoing monitoring tools that alert you to potential security issues before they trigger blacklisting. Regular scans identify suspicious activity patterns, enabling preventative action before problems escalate.
Free 7 days access to all tools. No credit card required!
Попробовать бесплатно
Final Verdict
URL blacklisting represents a significant digital obstacle that can severely impact your website’s visibility and brand reputation. Whether caused by malware, spam, or outdated security practices, blacklisting results in traffic loss and damaged user trust.
The good news? Blacklisting isn’t permanent if you take appropriate action. Understanding the primary causes – phishing schemes, SEO spam, malware, and unsafe plugins – helps you implement effective preventative measures.
Key preventative strategies include:
- Keeping all systems updated with the latest security patches
- Using only trusted software from reputable developers
- Implementing strong passwords and login attempt limitations
- Utilizing scanning tools to identify potential threats early
If blacklisting occurs despite these precautions, follow the recovery process:
- Thoroughly clean your website of all malicious content
- Request review from the relevant blacklisting authorities
- Implement stronger security measures to prevent recurrence
Remember that blacklisting serves an important purpose – protecting internet users from potentially harmful sites. By maintaining strong security practices, you not only avoid blacklisting but also contribute to a safer online environment.
Proactive security measures always prove more cost-effective than recovery efforts. The investment in prevention helps maintain consistent traffic, preserve user trust, and avoid the significant business disruption that blacklisting causes.
FAQs
What is an URL blacklist?
A URL blacklist is a database of websites flagged as potentially harmful by search engines, antivirus providers, or security services. These sites are identified as containing malware, phishing schemes, or other security threats that could harm visitors. Users attempting to access blacklisted sites typically see warning messages advising them to leave.How do I unblock a URL blacklist?
To unblock a blacklisted URL, first identify and remove all malicious content or code from your website. After cleaning your site thoroughly, request a review through Google Search Console or the relevant blacklisting authority. Provide detailed information about the steps taken to resolve the issues. Upon successful review, your site will be removed from the blacklist.What does it mean if something is infected with URL blacklist?
If your site is “infected with URL blacklist,” it means security services have identified potential threats on your website and added it to their warning databases. This isn’t an infection itself but rather a consequence of having malware, phishing content, or other security issues on your site that have triggered blacklisting by protection services.Why is my URL blacklisted?
Your URL might be blacklisted due to malware infections, phishing content, SEO spam, or unsafe plugins. Sometimes hackers inject malicious code without your knowledge. Other times, outdated software creates vulnerabilities exploited by attackers. Regular security scanning helps identify the specific cause, which is the first step toward resolution.How do I fix blocked URL?
To fix a blocked URL, first scan your website thoroughly to identify all security issues. Remove any malware, phishing content, or spam injections. Update all software, plugins, and themes to their latest versions. Strengthen passwords and security settings. Finally, request a review from Google Search Console or other blacklisting authorities to have your site removed from their warning lists.






